 THE MINERAL RHABDOPHANE
THE MINERAL RHABDOPHANE
- Chemistry: (Ce, La, Nd)PO4 - H2O, Hydrated Cerium Lanthanum Neodymium Phosphate.
- Class: Phosphates
- Group: Rhabdophane
- Uses: As a minor ore of cerium and as mineral specimens.
Specimens
Rhabdophane is one of several rare earth phosphate minerals. Xenotime - (Y), monazite, churchite - (Y),
Rhabdophane is actually a collection of three officially recognized minerals that are distinguished by their percentages of rare earth elements. Each is named for the rare earth element that composes the highest percentage of rare earth elements in that particular mineral. The three minerals are Rhabdophane - (Ce), Rhabdophane - (La), Rhabdophane - (Nd) All are very similar and difficult to distinguish. Most rhabdophane specimens are rhabdophane - (Ce) and this is most likely the mineral that is referred to when specimens are labeled simply as "rhabdophane".
Rhabdophane lends its name to a small group of phosphates. All members of the Rhabdophane Group are hexagonal or pseudo-hexagonal and have a general formula of (X)PO4 - 1-2H2O. The X can be either calcium, cerium, lead, lanthanum, neodymium, thorium, iron and uranium. Some sulfate ions, (SO4), can replace a portion of the phosphate ions, (PO4).
These are the members of the Rhabdophane Group:
Brockite (Hydrated Calcium Thorium Cerium Phosphate)Grayite (Hydrated Thorium Lead Calcium Phosphate)Ningyoite (Hydrated Uranium Calcium Cerium Phosphate)- Rhabdophane - (Ce) (Hydrated Cerium Lanthanum Phosphate)
- Rhabdophane - (La) (Hydrated Lanthanum Cerium Phosphate)
- Rhabdophane - (Nd) (Hydrated Neodymium Cerium Lanthanum Phosphate)
Tristramite (Hydrated Calcium Uranium Iron Phosphate Sulfate)
PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS:
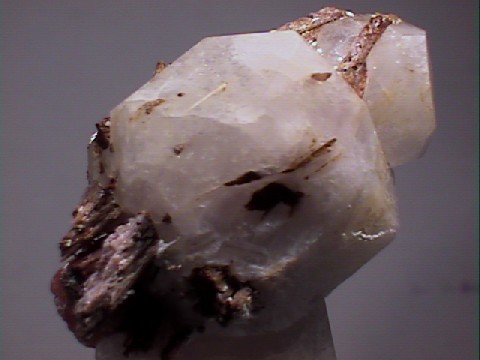
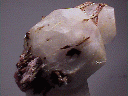
- Color is white, yellowish, pink to reddish brown.
- Luster is greasy to dull.
- Transparency: Specimens are translucent.
- Crystal System is hexagonal; 6 2 2.
- Crystal Habits include tiny hexagonal prisms but more commonly found as encrusting, massive, botryoidal and stalactitic formations.
- Cleavage is absent.
- Fracture is uneven.
- Hardness is 3.5 - 4.
- Specific Gravity is approximately 4.0 (above average for translucent minerals)
- Streak is white.
- Associated Minerals include limonite, serandite, amphiboles, natrolite, aegirine, astrophyllite, albite, calcite, biotite, rhodochrosite and rare earth granitic minerals.
- Notable Occurrences include Majuba Hill, Pershing County, Nevada and
Salisbury, Litchfield County, Connecticut, USA; Gakaia, Burundi: Fowey Consols,
Cornwall , England; Grube Clara, Oberwolfach, Germany; Mt Weld, Western Australia; Kola Peninsula, Russia and Mont Saint-Hilaire, Quebec, Canada. - Best Field Indicators are crystal habit, color, luster and locality.