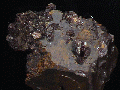THE MINERAL LIMONITE
THE MINERAL LIMONITE
- Chemistry: A mixture of hydrated iron oxides
- Class: Oxides and Hydroxides
- Uses: Important ore of iron, as a pigment and as mineral specimens.
- Specimens
Limonite is not a true mineral but a mixture of similar hydrated iron oxide minerals.
Most of limonite is made up of
Goethite.
Massive Goethite and Limonite can be indistinguishable.
Limonite forms mostly in or near oxidized iron and other metal ore deposits, and as sedimentary beds.
Limonite has been known to pseudomorph other minerals such as
pyrite,
meaning it replaces a crystal of pyrite with limonite but keeps the shape of the pyrite crystal.
PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS:
- Color is yellow, orange, reddish brown, brownish black.
- Luster is earthy to dull.
- Transparency is opaque.
- Crystal System is undefined.
- Crystal Habits include massive, layered, botryoidal and stalactitic.
- Cleavage is absent.
- Fracture is crumbly or earthy.
- Hardness is variable 4 - 5.5
- Specific Gravity is variable at 2.9 to 4.3 (average to above average)
- Streak is brownish yellow to yellow.
- Associated Minerals include a large list of minerals particularly secondary deposit minerals.
- Notable Occurrences include many iron mines around the world, especially nice specimens come from Europe, Mexico, Canada and northeastern USA.
- Best Field Indicators are lack of crystal forms, lack of cleavage and streak.
 THE MINERAL LIMONITE
THE MINERAL LIMONITE