 THE MINERAL ANGLESITE
THE MINERAL ANGLESITE
Anglesite is named for its type locality of Anglesey, an island at the northern tip of the United Kingdom. It is a secondary mineral, typically formed in the oxidation zone of galena (lead sulfide) ores.
PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS:
- Color is usually colorless, white and yellow; also pale gray, blue and green.
- Luster is adamantine.
- Transparency crystals are transparent to translucent.
- Crystal System is orthorhombic; 2/m 2/m 2/m
- Crystal Habits include the bladed or tabular crystals that are dominated by two large pinacoid faces top and bottom and small prism faces forming a jutting angle on every side. There are many variations of these faces and complex forms can occur. If the pinacoid faces become diminished or are absent, the resulting prismatic crystal has a rhombic cross section.. Anglesite typically forms a flattened blade that juts out from a host rock and with what appears to be a steep dome termination but is actually two faces of another rhombic prism. Also forms crusts and is granular and massive.
- Cleavage is perfect in one direction, less so in two other directions.
- Fracture is conchoidal.
- Hardness is 2.5 - 3.
- Specific Gravity is approximately 6.3+ (very heavy for translucent minerals)
- Streak is white.
- Associated Minerals are galena, cerussite, barite and limonite.
- Other Characteristics: Index of refraction is 1.88+ (very high), some specimens fluoresce yellow under UV light.
- Notable Occurances include Tsumeb, Nambia; Australia; England, Mexico and Toussit, Morocco.
- Best Field Indicators are crystal habit, density, high luster and color.
 Amethyst Galleries' Mineral Gallery MINERALS |

ANGLESITE specimen ang-1
$ 60.00
$ 60.00
Dims: 3" x 2-1/2" x 2"
Wt: 21.6 oz
Toussit, Morocco
This inordinately heavy specimen is graced by a cluster of near-perfect botryoidal tablets. These crystals are pale yellow and incredibly clear, and are cradled in a hollow in the Galena matrix, which makes up most of the specimen's weight. There also seems to be a negligible touch of calcite with a rust(?) coating. These Anglesites are very pretty; no collection should be without one.

ang-1 ($ 60.00)
Toussit, Morocco

ANGLESITE specimen ang-2
$ 30.00
$ 30.00
Dims: 2-1/2" x 2-1/4" x 2"
Wt: 1 lb
Toussit, Morocco
Hidden away in a protective depression in a hunk of Galena, are nestled several crystals of shiny, yellow, transparent Anglesite. Most of these crystals are damaged to some extent, but a few are nearly perfect in cleanliness and symmetry. Along one side of the specimen are many remains of broken crystals, and scattered on all sides are occasional minute pockets lined with tiny crystals... quite pretty!
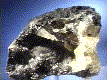
ang-2 ($ 30.00)
Toussit, Morocco

ANGLESITE specimen ang-3
$ 45.00
$ 45.00
Dims: 3.9" x 3.5" x 2.1"(9.9 x 8.9 x 5.3 cm)
Wt: 2 lbs., 11.2 oz.(1.224 kg)
Toussit, Morocco
The sparkle of at least 20 perfect Anglesite crystals is easy to see in the hollow on this ponderous specimen. They range in size from a few millimeters to 0.7"(1.8 cm) in length. All of them have a pale yellow color and an adamantine luster. The only aspect that interferes with their perfect transparency is the fact that each flat, prismatic crystal has heavy striations running along its prism faces. Only the crystals along the very edge of the hollow show any damage. The base material that holds the crystals is made up almost entirely of galena(at least it FEELS that way!), so the specimen is very heavy. There is a lot of exceptional Anglesite in this specimen, more than I have seen on others that we have sold.

ang-3 ($ 45.00)
Toussit, Morocco

ANGLESITE specimen ang-4
$ 30.00
$ 30.00
Dims: 3.0" x 3.2" x 1.8"(7.6 x 8.1 x 4.6 cm)
Wt: 1 lbs., 3 oz.(540 g)
Toussit, Morocco
These are some of the more unusual crystals of Anglesite that I have seen. They have the classic prismaitic form with wedge-shaped terminations of Anglesite, but their color is an odd, light brown-orange color. This coloration is due to inclusions in the crystals that may actually be made up of rust! These inclusions drastically reduce the crystals' transparence to "translucent-to-opaque" status. These inclusions also seem to affect the crystals' luster, making them appear vitreous to waxy, instead of adamantine. These crystals range in size from 2-3 mm to 1"(1.3 cm) in length. One of the larger crystals has very clean termination faces, allowing one to see into it. There is a phantom visible through these faces, the same shape as the crystal it encloses. There are phantoms visible in one or two more crystals, but most of them have cloudy termination faces. There is some noticeable damage to some of the crystals, but they are generally in good condition. They all rest in a hollow in a galena matrix, which makes the specimen very heavy.

ang-4 ($ 30.00)
Toussit, Morocco

ANGLESITE specimen ang-5
$ 22.00
$ 22.00
Dims: 2.5" x 2.2" x 1.7" (6.4 x 5.6 x 4.3 cm)
Wt: 12.4 oz. (351 g)
Toussit, Morocco
The most impressive crystals on this specimen are not necessarily the most noticeable. The largest crystals are quite visible against the dark gray galena base, but all of these are damaged and broken. However, there are many more small crystals that have perfect form and are intact. One of these measures 0.9 x 0.1 x 0.1" (2.3 x 0.3 x 0.2 cm); I am quite surprised that it has not been broken. The others are smaller and a bit more difficult to see, as they are a pale yellow color, transparent, and quite clear, so that they blend in well with the dark background. They all occur as thin, bladed orthorombic crystals with an adamantine luster; this luster is what makes them most easily visible.

ang-5 ($ 22.00)
Toussit, Morocco

ANGLESITE specimen ang-6
$ 33.00
$ 33.00
Dims: 3.0" x 2.9" x 1.6" (7.6 x 7.4 x 4.1 cm)
Wt: 1 lb., 9.8 oz. (789 g)
Toussit, Morocco
This specimen consists of a rather flat, square-shaped piece of galena that acts as a matrix rock; one corner of the piece of galena is missing, and the resulting depression is partially lined with Anglesite crystals. These crystals occur as flat, tabular to prismatic crystals with rather steep, wedge-shaped terminations. Though many are incomplete due to growth against the host rock (part of which has been removed), there is very little evidence of human-induced damage. These crystals range in size from a few millimeters to nearly 0.5" (1.3 cm) in length, and in color from colorless to a moderately pale yellow. All have an adamantine luster and are transparent and very clear, though showing considerable internal fracturing. Trapped throughout the galena matrix are many other pieces of Anglesite, but all are broken, incomplete, and almost completely embedded. There is also a substantial amount of a yellow, powdery substance coating parts of the galena, which is likely a decomposition product.

ang-6 ($ 33.00)
Toussit, Morocco

ANGLESITE specimen ang-7
$ 24.00
$ 24.00
Dims: 1.8" x 1.3" x 1.0" (7.6 x 7.4 x 4.1 cm)
Wt: 2.34 oz. (66.5 g)
Toussit, Morocco
Though this Anglesite specimen's crystals are rather small and their intergrowth warps and interrupts their form, they still create a pretty and interesting specimen. There are at least 9 separate and distinct crystals on this specimen, ranging from 0.2" (5 mm) to 1.0" (2.5 cm) in length. Though very heavily intergrown, definite termination faces are visible on nearly every crystal, and there is only moderate visible damage. A thin green-gray crust covers part of the cluster's surface, and likely represents the point where the cluster was attached to its host rock. The crystals have the standard pale yellow color and vitreous-to-adamantine luster that is characteristic of Anglesite. They are all transparent and quite clear, though many internal fractures are visible. It is a pleasant little specimen that is appropriate for somebody who wants a token specimen of this mineral in their collection that is still of decent quality.

ang-7 ($ 24.00)
Toussit, Morocco

ANGLESITE specimen ang-8
$ 95.00
$ 95.00
Dims: 2.7" x 1.9" x 1.0" (6.9 x 4.8 x 2.5 cm)
Wt: 6.84 oz. (194.0 g)
Toussit, Morocco
At least 10 small Anglesite crystals rest in a hollow on one edge of the flat galena host of this specimen. They are in generally good condition, though a few are obviously damaged, and they measure up to 0.5" (1.3 cm). Their orthorombic prismatic form is excellent, with well-defined edges and clean, smooth faces that show their adamantine luster. They are colorless, transparent, and very clear- there are few visible inclusions or internal flaws. There are broken portions of crystals in other parts of the galena host, but there is no other foreign material.


ang-8 ($ 95.00)
Toussit, Morocco

$ 205.00
Dims: 2.5" x 1.2" x 0.9" (6.4 x 3.0 x 2.3 cm)
Wt: 2.84 oz. (80.7 g)
Toussit Mine, Oujda, Morocco
There are several Anglesite crystals growing off of the galena base of this specimen. Though several of the crystals are damaged and incomplete, those that are intact are in excellent condition, with almost no visible damage. These intact crystals are larger than most that I have seen- one of them measures 0.6 x 0.6 x 0.2" (1.5 x 1.5 x 0.5 cm). They have excellent orthorombic bladed form with sharp edges and striated but clean faces that show a bright, adamantine luster. They all have a pale yellow coloration and are transparent and remarkably clear, showing almost no internal fractures. The galena base seems to have a rather thick layer of a soft, chalky white mineral partially covering it that may well be a lead oxide. These are some of the best Anglesite crystals that we have been able to find.


Toussit Mine, Oujda, Morocco

ANGLESITE specimen ang-10
$ 110.00
$ 110.00
Dims: 1.5" x 1.3" x 0.9" (3.8 x 3.3 x 0.9 cm)
Wt: 1.37 oz. (38.9 g)
Level 11, Bunker Hill Mine, Kellogg, Idaho, U.S.A.
I cannot define the variation of this Anglesite crystal's orthorhombic prismatic form- it is just a bit ttoo warped and irregular for my eye. There are two Anglesites on this specimen, both of which appear to be very odd as far as form is concerned. They are in excellent condition, however, showing almost no detectable damage. The larger has dimensions of 1.0 x 0.5 x 0.5" (2.5 x 1.3 x 1.3 cm), whereas the smaller measures 0.3 x 0.3 x 0.2" (8 x 8 x 5 mm). Their forms, though odd, show well-defined edges and clean faces that have a bright, pearly luster. The larger crystal has a pale, creamy coloration and is translucent. The smaller crystal has a much darker, gray coloration that is likely caused by the crystal taking on some finely divided galena particles during its formation. Both crystals rest on a base of galena that is very dark, dull, and weathered and shows its gray color and metallic luster only through a damaged area.

ang-10 ($110.00)
Level 11, Bunker Hill Mine, Kellogg, Idaho, U.S.A.

ANGLESITE specimen ang-11
$ 45.00
$ 45.00
Dims: 2.5" x 2.3" x 1.6" (6.4 x 5.8 x 4.1 cm)
Wt: 11.1 oz. (314 g)
Toussit, Morocco
At least 18 Anglesite crystals are intergrown to form a druse that partially coats the galena host rock of this specimen. These crystals range in size from 2 or 3 mm along any axis to some whose visible dimensions all exceed 0.5" (1.3 cm). Most of the larger and more exposed crystals show damage in one form or another, and some are very much incomplete. Those that are intact show good orthorhombic prismatic form and have well-defined edges and clean faces that show a vitreous luster. They are colorless, transparent and moderately clear, with noticeable inclusions and internal fracturing. The galena base on which they rest has a dark gray color and a dull, waxy luster that is indicative of weathering and exposure. It shows no discernable crystal form.

ang-11 ($ 45.00)
Toussit, Morocco

ANGLESITE specimen ang-12
$ 70.00
$ 70.00
Dims: 1.0" x 0.9" x 0.8" (2.5 x 2.3 x 2.0 cm)
Wt: 27.1 g w/ base
Toussit, Oudja, Morocco
There are at least 9 discernable Anglesite crystals resting on the sparse galena base of this small thumbnail specimen. All are in excellent condition, showing almost no damage whatsoever, and the largest has dimensions of 0.5 x 0.5 x 0.3" (1.3 x 1.3 x 0.8 cm). Though all are intergrown to a degree, they have exceptional orthorhombic form in an unusual prismatic habit, with multi-faced domed terminations. One of the larger crystals shows what appears to be a twinning plane that bisects its termination. All have a very subtle, pale yellow coloration and a bright, vitreous-to-adamantine luster. They are transparent and quite clear, showing only a few internal fractures. I have left the specimen in the state in which we acquired it, hot-glued to a small, square acrylic base.

ang-12 ($ 70.00)
Toussit, Oudja, Morocco

ANGLESITE specimen ang-13
$ 200.00
$ 200.00
Dims: 4.0" x 3.1" x 2.2" (10.2 x 7.9 x 5.6 cm)
Wt: 2 lbs., 4.7 oz. (1.041 kg)
Toussit, Oudja, Morocco
Resting in a hollow in the massive galena host rock of this specimen are at least 20 orthorhombic prismatic Anglesite crystals. These crystals range in size from 2mm x 2mm x 2mm or less up to 0.5 x 0.4 x 0.3" (1.3 x 1.0 x 0.8 cm), and all are in perfect condition, being sheltered inside their hollow. Their form is excellent, and all show sharp edges and very clean faces that show a bright, adamantine luster. Their color is somewhat difficult to determine due to the almost rusty coloration of a powdery substance that is present in the hollow, but they appear to have a very subtle, pale beige coloration that is slightly yellow. All are transparent and very clear, though the largest does contain one or two internal fractures. There are a few other small Anglesite druses scattered elsewhere on the galena base, but most of these are either very small or show considerable damage.


ang-13 ($200.00)
Toussit, Oudja, Morocco

ANGLESITE specimen ang-14
$ 100.00
$ 100.00
Dims: 3.8" x 2.3" x 1.5" (9.7 x 5.8 x 3.8 cm)
Wt: 1 lb., 9.7 oz. (728 g)
Toussit, Oudja, Morocco
Several pale yellow Anglesite crystals rest on the heavy galena base of this specimen. Though many of these crystals are damaged, most have only minor damage and only a few are obviously broken. They show excellent orthorhombic prismatic form, with well-defined edges and clean faces that possess an adamantine luster. All are transparent and very clear; only internal fractures provide any interference. The largest and most complete of these crystals has dimensions of 0.4 x 0.3 x 0.2" (1.0 x 0.8 x 0.5 cm). The galena base on which they rest is formless and essentially massive, but shows definite crystalline tendencies; a few shallow veins of colorless Anglesite penetrate it.


ang-14 ($100.00)
Toussit, Oudja, Morocco

ANGLESITE specimen ang-15
$ 160.00
$ 160.00
Dims: 2.0 x 1.3 x 0.9" (5.1 x 3.3 x 2.3 cm)
Wt: 2.58 oz. (73.0 g)
Toussit, Oudja, Morocco
There are likely no more than 10 Anglesite crystals resting on the galena base of this large thumbnail specimen. However, the most exposed of these crystals are exceptional, both in size and quality. The largest of them has dimensions of 0.8 x 0.7 x 0.2" (2.0 x 1.8 x 0.5 cm) and is in pristine condition, showing no visible damage. One other crystal is only slightly smaller, and though it has the most damage of all the intact crystals on the piece, it is still in good condition. Their orthorhombic bladed form is excellent, with well-defined edges and striated but clean faces that possess a bright, almost adamantine luster. Their color is a pale, watery yellow, and all are transparent and very clear, containing only a few veil-like inclusions and the occasional internal fracture as interference. There are a few larger crystals on the piece, but these are broken and mostly incomplete. The base is not just made up of galena- there is also a white, powdery material on it that may be some type of lead oxide.


ang-15 ($160.00)
Toussit, Oudja, Morocco

ANGLESITE specimen ang-16
$ 25.00
$ 25.00
Dims: 3.4 x 2.5 x 1.8" (8.6 x 6.4 x 4.5 cm)
Wt: 6.59 oz. (187.0 g)
Toussit, near Oudja, Morocco
Several Anglesite crystals extend from the galena base of this hand specimen. Almost all are broken and incomplete- only 3 or 4 small crystals are intact. All have good orthorhombic prismatic form where intact, and their pale yellow color and adamantine luster are common for the species. They are translucent and moderately clear- most of the larger, broken crystals are heavily internally-fractured. The galena base shows definite crystal form in some areas, but most of the crystals are small and heavily intergrown.

ang-16 ($ 25.00)
Toussit, near Oudja, Morocco

ANGLESITE specimen ang-17
$ 69.00
$ 69.00
Dims: 1.3x1.5x0.8" (3.3x3.9x2.0cm)
Wt: 1.77 oz. (50.0g)
Toussit, Oudja, Morocco
A single very large anglesite crystal (and a few small ones) are perched upon a base of intergrown galena crystals. That large crystal is excellent, although its thin edges are significantly damaged. The crystal is mostly transparent and colorless, with black areas (from galena inclusions) near its base, and a yellow color on the sides near the termination. That termination itself is excellent, with no significant damage or flaws. Close examination reveals that the two sides are slightly offset, leaving extra crystal edges where points might otherwise have been.

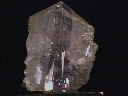
ang-17 ($ 69.00)
Toussit, Oudja, Morocco

ANGLESITE specimen ang-18
$ 35.00
$ 35.00
Dims:
Wt: 4.91oz (139.3g)
Toussit, Oudja, Morocco
Several excellent anglesite crystals are nestled in a cavity of a dense host rock. The anglesite crystals are yellow, transparent, and highly lustrous with no sign of damage visible to the unaided eye. There are some internal fractures marring the transparency of the crystals. There are actually dozens of anglesite crystals, but most are tiny or aligned flat against the substrate. The host rock appears to be a granular galena. There is also a yellow mineral crust present which I have not identified, although the specimen has a distinct sulfur smell which could indicate the presence of elemental sulfur or marcasite, among others.


ang-18 ($ 35.00)
Toussit, Oudja, Morocco

ANGLESITE specimen ang-19
$ 30.00
$ 30.00
DIMS mm=41.76x34.93x22.97
WT G=58.7
Morroco
A matrix of fractured galena hosts a number of intergrown crystals of anglesite, the largest of which exceeds 13mm in length. These are colorless and quite transparent, and while most show some damage, they are in excellent overall condition.


ang-19 ($ 30.00)
Morroco