 THE MINERAL GMELINITE
THE MINERAL GMELINITE
- Chemistry: (Na2, Ca)Al2Si4O12 - 6H2O, Hydrated sodium calcium aluminum silicate
- Class: Silicates
- Subclass: Tektosilicates
- Group: Zeolites
- Uses: Mineral specimen and chemical filter.
Specimens
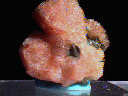
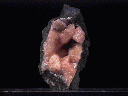
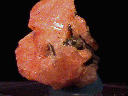
Crystals of gmelinite have a unique shape that could be described as being an angular version of a classic UFO flying saucer. It is hexagonal in outline and is dominated by a dipyramid (two identical pyramids at the top and bottom). However, the faces of the pyramids are relatively gentle in slope and are capped by a flat pedion face.
PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS:
- Color is clear, white, pink, yellowish and reddish.
- Luster is vitreous.
- Transparency: Crystals are transparent to translucent.
- Crystal System is hexagonal.
- Crystal Habits include tabular to platy crystals with a clear hexagonal outline.
The crystals have a gently sloping hexagonal
dipyramid that terminates the top and bottom of the crystal that are often truncated by pinacoidal faces. The overall effect gives the look of an angular classic UFO flying saucer. Twinning is common with penetration twins. - Cleavage is absent.
- Fracture is uneven.
- Hardness is 4.5.
- Specific Gravity is approximately 2.0 - 2.1 (very light)
- Streak is white.
- Other Characteristics: Vertical striations are seen on the dipyramidal faces.
- Associated Minerals are quartz, calcite, chabazite, phillipsite, natrolite, heulandite, stilbite and other zeolites.
- Notable Occurrences include Siegerland, Germany; Glenarm, Northern Ireland; New Jersey and Faroe Islands.
- Best Field Indicators are crystal habit, density, hardness and associations.