 THE MINERAL EPIDOTE
THE MINERAL EPIDOTE
- Chemistry: Ca2(Al, Fe)3(SiO4)3(OH), Calcium Aluminum Iron Silicate Hydroxide.
- Class: Silicates
- Subclass: Sorosilicates
- Group: Epidote
- Uses: mineral specimens and rarely as a gemstone.
Specimens
PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS:
- Color is "pistachio" green to yellowish or brownish green, also brown to black.
- Luster is vitreous.
- Transparency crystals are transparent to translucent.
- Crystal System monoclinic; 2/m
- Crystal Habits include long, somewhat prismatic or tabular crystals with a typically dominant pinacoid that the crystal is often flattened against. The terminations are wedge shaped or tappered pyramids. Many clusters show grooved slender crystals or acicular sprays. Also massive, fiberous or granular.
- Cleavage good in one direction lengthwise.
- Fracture is uneven to conchoidal.
- Hardness is 6-7
- Specific Gravity is 3.3-3.5
- Streak white to gray
- Associated Minerals calcite, biotite, hornblende, actinolite, andradite garnet and other metamorphic minerals.
- Other Characteristics: striated to the depth of grooves in some crystals.
- Notable Occurances Untersulzbachtal, Austria; Italy; Baja, Mexico and many localities in the USA.
- Best Field Indicators only one direction of cleavage, crystal habit, color and hardness.
 Amethyst Galleries' Mineral Gallery MINERALS |

EPIDOTE specimen epi-1
$ 90.00
$ 90.00
Dims: 5" x 4-7/8" x 2-1/2"
Wt: 2 lbs., 8 oz
Minas Gerais, Braz.
This incredible specimen of Epidote is dominated by a crystal 4 inches long by 2 inches wide that is very heavily fractured, and somewhat flaky. But for that reason, this piece would easily pass for gem-quality, with its deep forest-green color and its excellent clarity. The crystals themselves show good, clean faces and distinct, though very incomplete terminations. It's a superb specimen that could earn a place in a small museum collection.

epi-1 ($ 90.00)
Minas Gerais, Braz.

EPIDOTE specimen epi-2
$ 30.00
$ 30.00
Dims: 3-1/2" x 2-1/2" x 1-1/2"
Wt: 11.4 oz
Minas Gerais, Braz.
Although this specimen is highly fractured, and thus rather delicate, it is very attractive, with its dark forest-green color against a clear Quartz background. It is mostly Epidote by weight, and shows no crystal form due to fragmentation.
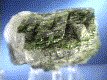
epi-2 ($ 30.00)
Minas Gerais, Braz.

EPIDOTE specimen epi-3
$ 48.00
$ 48.00
Dims: 3" x 2-1/2" x 2"
Wt: 2.5 oz
Minas Gerais, Brazil
This specimen has some of the best crystal form of our Epidote selection. While not having a complete termination, part of the crystals length is almost whole, showing a beveled edge that upon first glance looks rounded. This specimen is less fractured than most, and thus the crystals show a darker shade of forest green that approaches black in some areas.

epi-3 ($ 48.00)
Minas Gerais, Brazil

EPIDOTE specimen epi-4
$ 25.00
$ 25.00
Dims: 3" x 2-1/2" x 2"
Wt: 6.8 oz
California, U.S.A.
This neat little Californian specimen has one of the best crystal forms that I have seen for epidote. The main attraction is a crystal that grew outward as well as upward, but not long enough for it to split up into several smaller crystals. The color is black with spinach-green highlights that show due to the rampant fracture lines. The termination is excellent, with a layered, concentric rise from the outer edge to the center of its face. The large crystal has grown almost parallel to the main face of the host rock, laying on its side atop a bed of small dogtooth Calcites. Steve and I both like this specimen immensely- it is very pleasant to look at.

epi-4 ($ 25.00)
California, U.S.A.

EPIDOTE specimen epi-5
$ 30.00
$ 30.00
Dims: 3.2" x 2.3" x 1.6" (8.1 x 5.8 x 4.1 cm)
Wt: 7.65 oz. (217.0 g)
Minas Gerais, Brazil
Although this Epidote specimen does not contain any complete, intact, crystals, two of them have enough material so that one can discern their monoclinic prismatic form and shallow, three-faced pyramidal terminations. All show heavy damage, giving the rest of the material indeterminate form. The Epidote's color is a deep forest green, and its luster is pearly to vitreous. Its faint translucence is likely almost completely interrupted by the intense internal fracturing that is present. This material makes up about half of the specimen's mass- the other half is made up of milky-white, massive quartz.

epi-5 ($ 30.00)
Minas Gerais, Brazil

EPIDOTE specimen epi-6
$ 38.00
$ 38.00
Dims: 3.7" x 2.2" x 2.0" (9.4 x 5.6 x 5.1 cm)
Wt: 10.02 oz. (284.0 g)
Minas Gerais, Brazil
This specimen is made up of mostly Epidote by weight; they occur in the form of monoclinic prismatic crystals that are damaged and incomplete, but many prism faces are still visible. Their color is a deep forest green and they have a vitreous luster on their intact faces. All but one are dimly translucent, likely because of their heavy internal fracturing; the other crystal is quite small and thin, and shows definite transparence, though clarity is destroyed by more internal fractures. Amidst this broken cluster is a small amount of white, massive quartz. The color of the Epidote would make a pretty gemstone, if one could find a crystal or a piece of it that is not so broken up inside.

epi-6 ($ 38.00)
Minas Gerais, Brazil

EPIDOTE specimen epi-7
$ 22.00
$ 22.00
Dims: 3.2" x 2.4" x 2.0" (8.1 x 6.1 x 5.1 cm)
Wt: 8.60 oz. (244.0 g)
California, U.S.A.
This specimen represents some of the most mysterious material that I have ever seen. Though I am uncertain of its exact locality, I know that it comes from Calfornia, along the western border of the U.S.. It consists of a cluster of heavily intergrown andradite garnets that are hollow, so that their mass consists of only dodecahedral shaped "shells". Underneath the many broken areas on these shells, dozens of malformed Epidote crystals have grown. Most are either severely warped or broken, so that very little crystal form is discernable, but I think that that major flaw is overshadowed by the mystery of how this material formed in the way that it did. I really have no ideas as to how this could have occurred!


epi-7 ($ 22.00)
California, U.S.A.

$ 105.00
Dims: 3.0" x 2.8" x 1.5" (7.6 x 7.1 x 3.8 cm)
Wt: 3.12 oz. (88.5 g)
Castro Vireyna, Huancavelica, Peru
One of the more attractive Epidote specimens that I have seen, this piece consists of a cluster of thin, almost needle-like Epidote crystals that is partly intergrown with a hexagonal prismatic quartz crystal. These crystals range in length from 0.1 (3 mm) to nearly 2" (5 cm), but do not exceed 3 mm along either of their other axes. Many of them are damaged and incomplete, but those that are intact are easy to spot from light glinting off of their termination faces. Their monoclinic, prismatic form is excellent, and their terminations are well-formed, giving off a bright, vitreous luster. Their prism faces are striated and a bit duller, showing more of a pearly luster. Though some of the smaller, more exposed crystals show some noticeable transparence, their almost olive-green coloration is too deep to be even translucent in most cases. The intergrown quatrt crystal shows good hexagonal form, but its termination is completely enveloped by the Epidote cluster. Its other end its other end is slightly uneven but generally flat, and shows evidence of healing. It is colorless, transparent, and relatively clear, but 2 of its prism faces are very frosty, showing a matte luster; this makes it difficult to easily examine its interior. There is no evidence of any host rock.


Castro Vireyna, Huancavelica, Peru

EPIDOTE specimen epi-9
$ 60.00
$ 60.00
Dims: 2.2" x 2.0" x 1.2" (5.6 x 5.1 x 3.0 cm)
Wt: 2.69 oz. (76.3 g)
Castro Vireyna, Huancavelica, Peru
Several monoclinic prismatic Epidote crystals rest on the crystalline quartz base of this small hand specimen. These crystals do not exceed 1.3" (3.3 cm) in length, and many of them are damaged. However, those that are intact have excellent form, possessing well-defined edges and clean faces that show a bright vitreous luster. Their color is brownish-green, and all are translucent but have some areas of transparence. The base on which they rest consists of two partly intergrown quartz crystals that are incomplete due to both damage and intergrowth with crystals that have been since removed. They have a milky white color and a rather dull vitreous luster, and are moderately to dimly transparent. The base of these crystals shows some very interesting traits; a few bits of broken crystals project beyond its edges, and these look suspiciously like bits of andradite garnet. There are also small brownish crusts that coat small potions of the quartz's base, and broken bits of Epidote rest on top of them. This makes me think of some andradite specimens that I have seen in which the andradite forms a crust, underneath which rest tiny, incomplete Epidotes. Besides that, there are also several hexagonal "books" of hematite platelets gathered in one area, some of which appear to be complete!


epi-9 ($ 60.00)
Castro Vireyna, Huancavelica, Peru

EPIDOTE specimen epi-10
$ 105.00
$ 105.00
Dims: 3.1 x 3.0 x 0.8" (7.9 x 7.7 x 2.0 cm)
Wt: 4.92 oz. (139.7 g)
Castro Vireyna, Huancavelica, Peru
This specimen represents one of the finer Epidote clusters that I have seen in my travels. It is made up of scores of radiating, monoclinic prismatic crystals that are generally in excellent condition and reach lengths of up to 2.6" (6.6 cm). Their form is exceptional- all have well-defined edges, clean faces that possess a vitreous luster, and slightly offset, two-faced domed terminations. Their color is a uniform dark green with a noticeable brown tinge, and though individual crystals have a clarity that ranges from dimly translucent to dimly transparent, most are intensely intergrown, and thus essentially opaque. A few white rhombohedral calcites are attached along part of the prism area of the cluster, but there is no host rock present.


epi-10 ($105.00)
Castro Vireyna, Huancavelica, Peru

EPIDOTE specimen epi-11
$ 28.00
$ 28.00
Dims: 1.5 x 0.7 x 0.6" (3.8 x 1.8 x 1.5 cm)
Wt: 11.6 g
Namibia
This small thumbnail specimen consists of a "parallel association" that is made up of 2 large intergrown Epidote crystals, and about 4 or 5 smaller Epidotes. The specimen is in excellent condition, as there is almost no human-induced damage visible. The two intergrown crystals are nearly identical in size and form, and measure about 1.3" (3.3 cm) in length. They have excellent form, with well-defined edges and clean, smooth faces that possess a bright vitreous luster. They have a brownish-green coloration that is so deep that both crystals are opaque even in bright halogen light. The smaller crystals show translucence or even moderately good transparence depending on their size. The 2,largest crystals have an odd trait, however; as I was studying them under a halogen light, I noticed tiny, fibrous needles of some sort trapped just under the surface of one prism face on each crystal. I do not know what the material is made of. These prism faces both point in the same direction and are right next to each other. There is no host rock present.


epi-11 ($ 28.00)
Namibia

EPIDOTE specimen epi-12
$ 36.00
$ 36.00
Dims: 2.5 x 1.3 x 0.9" (6.4 x 3.3 x 2.3 cm)
Wt: 1.33 oz. (37.9 g)
Castro Vireyna, Huancavelica, Peru
This thumbnail specimen consists of 3 intersecting clusters of radiating Epidote crystals. These crystals achieve lengths of up to 2.5" (6.4 cm) and are in fair condition, as most of their terminations are either intergrown or broken off. Their monoclinic form is very good, even with their intense intergrowth- all have well-defined edges and clean faces that possess a bright vitreous luster. Their color is a deep brownish-green, and individually, each crystal would be transparent and probably partly clear. As a whole, however, the cluster is essentially opaque, though it shows translucence and even patches of transparence around its edges. There is no host rock present.

epi-12 ($ 36.00)
Castro Vireyna, Huancavelica, Peru

EPIDOTE specimen epi-13
$ 60.00
$ 60.00
Dims: 2.8 x 1.8 x 1.2" (7.1 x 4.6 x 3.0 cm)
Wt: 3.8 oz. (108.9 g)
Castro Vireyna, Huancavelica, Peru
A radiating cluster of partly intergrown Epidote crystals makes up this specimen. The crystals are generally in good condition, though there is considerable damage to one end of the cluster, and reach lengths of 2.8" (7.1 cm). The crystals have a moderately good form that shows considerable warping due to their intergrowth, especially at their terminations. However, their edges are still well-defined and their prism faces are clean and smooth, possessing a vitreous luster. All are essentially opaque- only a few of the thinnest and most exposed crystals show a dim translucence in halogen light. A few monoclinic albite crystals are attached to the cluster along the Epidotes' prism lengths, and there is a crust of a cream-colored, dull material that coats many of their terminations. There is no host or base material present, however.


epi-13 ($ 60.00)
Castro Vireyna, Huancavelica, Peru

EPIDOTE specimen epi-14
$ 45.00
$ 45.00
Dims: 2.2 x 1.6 x 0.9" (5.6 x 4.1 x 2.3 cm)
Wt: 1.9 oz. (55.1 g)
Castro Vireyna, Huancavelica, Peru
This large thumbnail specimen consists of a cluster of radiating Epidote crystals that are all intergrown towards their bases, and appear to emanate from a single point. The specimen is in good condition, as there is visible damage to several of the crystals' terminations, and the longest crystal does not exceed 2" (5 cm). Their form is good, but several of the crystals are rather warped in the fact that they appear to be twinned along their prism length (see the close-up image). Oddly enough, those twinned crystals are arranged in a straight line, so that their twinning planes form a single plane that runs through the entire cluster! All have a dark, greenish-black color with green highlights and a luster that ranges from waxy to vitreous. They are also opaque and there is no host rock present, though there are a few tiny smatterings of a dull tan material lining the crevices between crystals. I have never seen twinned crystals aligned together like this before.


epi-14 ($ 45.00)
Castro Vireyna, Huancavelica, Peru

EPIDOTE specimen epi-15
$ 70.00
$ 70.00
Dims: 2.5 x 2.1 x 2.0" (6.4 x 5.3 x 5.1 cm)
Wt: 3.0 oz. (84.1 g)
Castro Vireyna, Huancavelica, Peru
This small hand specimen consists of two partly intergrown clusters of radiating prismatic Epidote crystals. These crystals do not exceed 2.4" (6 cm) in length, and are generally in fair condition, as most are broken and missing their terminations. Those that are intact, however, have good monoclinic prismatic form, with well-defined edges and clean faces that possess a vitreous luster. The largest intact crystal shows obvious evidence of twinning, as can be seen by the striations on its "basal" face. All have a deep greenish-black coloration and are essentially opaque. There is one large, amorphous piece of broken quartz attached to the clusters and a few tiny crystals scattered elsewhere, but no other base or host material is present.

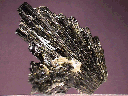
epi-15 ($ 70.00)
Castro Vireyna, Huancavelica, Peru

EPIDOTE specimen epi-16
$ 90.00
$ 90.00
Dims: 2.0 x 1.4 x 0.9" (5.1 x 3.6 x 2.3 cm)
Wt: 25.1 g
Castro Vireyna, Huancavelica, Peru
This thumbmnail-sized specimen consists of a cluster of heavily intergrown, radiating Epidote crystals that extends from a quartz-and-epidote base. These crystals are in excellent condition, as only one or two show any visible damage. The largest of these crystals measures 1.4" (3.6 cm) long, and though all are heavily intergrown, their monoclinic prismatic form is very good, with relatively well-defined edges and clean faces that show a moderate to dull vitreous luster. All have a dark greenish-black coloration and are essentially opaque. The base from which they extend is made up primarily of broken bits of Epidote and quartz crystals, and are covered by a cream-colored, dull crust that I cannot identify.
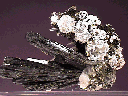
epi-16 ($ 90.00)
Castro Vireyna, Huancavelica, Peru

$ 60.00
Dims: 1.2 x 0.7 x 0.3" (3.0 x 1.8 x 0.8 cm)
Wt: 8.3 g w/ base
Hashupa, Shigar Valley, Baltistan, N.A., Pakistan
This small Epidote specimen is one of the more impressive ones that I have seen. It consists of two intersecting linear clusters of nearly parallel Epidote crystals. The two clusters intersect each other at nearly a 45-degree angle and are in excellent condition, showing almost no damage. Each crystal has excellent monoclinic prismatic form- all edges are very well-defined, and all faces are clean and possess a vitreous luster. Their color is a uniform, deep olive-green with a hint of brown, and all are transparent and impressively clear, containing few internal fractures and inclusions. There is no host rock present, and the piece is attached to an acrylic base with a removable adhesive putty.
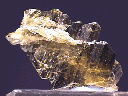
Hashupa, Shigar Valley, Baltistan, N.A., Pakistan