THE MINERAL ANDRADITE
THE MINERAL ANDRADITE
- Chemistry: Ca3Fe2(SiO4)3, Calcium iron silicate
- Class: Silicates
- Subclass: Nesosilicates
- Group: Garnets
- Uses: Gemstone and abrasive
- See our natural
Andradite Mineral Specimens
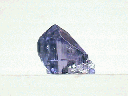
Andradite, like other garnets, forms rounded crystals with 12 rhombic or 24 trapezoidal faces or combinations of these and some other forms. This crystal habit is classic for the garnet minerals. Andradite is the calcium iron garnet and forms in contact or regional metamorphic environments as does grossular, the calcium aluminum garnet. It is believed that these garnets form from the metamorphism of impure siliceous limestones.
Andradite has many varieties based on color.
- Melanite is the black variety.
- Demantoid is the bright green variety and is sometimes cut as a gem.
- Topazolite is the yellow variety and is also occasionally cut as a gem.
PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS:
- Color is typically greenish gray to green but also black, yellow and rarely colorless.
- Luster is vitreous.
- Transparency crystals are transparent to translucent.
- Crystal System is isometric; 4/m bar 3 2/m
- Crystal Habits include the typical rhombic dodecahedron. also seen is the 24 sided trapezohedron. Combinations of these forms are common and sometimes the rare faces of the hexoctahedron, a 48 sided crystal habit that rarely is seen by itself, can also combine with these other forms making very attractive, complex and multifaceted crystals. Massive occurrences are also common. Commonly forms crust that shows many rhombic faces.
- Cleavage is absent.
- Fracture is conchoidal.
- Hardness is 6.5 - 7.5
- Specific Gravity is approximately 3.8+ (above average for translucent minerals).
- Streak is white.
- Associated Minerals are micas, chlorite, diopside and serpentine.
- Other Characteristics: index of refraction is 1.89 (highest of the garnets)
- Notable Occurrences include Arizona; Ural mountains in Russia; Italy and California..
- Best Field Indicators are crystal habit, color, index of refraction and hardness.