 THE MINERAL LEGRANDITE
THE MINERAL LEGRANDITE
- Chemistry: Zn2AsO4(OH) - H2O, Hydrated Zinc Arsenate Hydroxide
- Class: Phosphate Class
- Subclass: Arsenates
- Uses: Only as mineral specimens
- Specimens
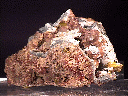
Legrandite is a rare and beautiful mineral that is a favorite of mineral collectors.
It is known world wide from the famous localities around Mapimi, Mexico.
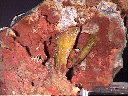
Legrandite is a vitreous mineral that seems to radiate its unusually rich yellow color.
No other mineral is associated with limonite that has a bright yellow color with prismatic crystals and therefore legrandite is pretty easy to identify.
However it is rare and not so easy to find.
Good specimens are hoarded by the collectors who are lucky enough to find them.
PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS:
- Color is straw to orange yellow to colorless.
- Luster is vitreous.
- Transparency: Crystals are transparent to translucent.
- Crystal System is monoclinic; 2/m
- Crystal Habits include prismatic to bladed crystals with a wedge shaped termination often complexly faceted.
- Cleavage is poor in one direction.
- Fracture is uneven.
- Hardness is 4.5 - 5.
- Specific Gravity is approximately 4.0 (above average for translucent minerals)
- Streak is white.
- Associated Minerals are
adamite,
limonite,
pyrite,
sphalerite,
smithsonite,
austinite,
paradamite,
aragonite,
calcite,
mimetite
and other oxidation zone minerals.
- Notable Occurrences include the famous mines at Mapimi,
Mexico as well as Flor de Pena Mine, Mexico.
- Best Field Indicators are color, luster, density,
associations and crystal habits.
 THE MINERAL LEGRANDITE
THE MINERAL LEGRANDITE