 THE MINERAL HANKSITE
THE MINERAL HANKSITE
- Chemistry: Na22K(SO4)9(CO3)2Cl, Sodium Potassium Sulfate Carbonate Chloride
- Class: Sulfates
- Uses: Only as mineral specimens
Specimens
Hanksite forms very nice crystals in evaporite deposits. These evaporite deposits occur in arid environments. Water, carrying dissolved minerals, floods into a dry lake beds and then just sits. The arid conditions evaporate the water and concentrate the ions. When the water is almost gone, crystals start to form. The mineral halite (salt) is one of the first minerals to crystallize. As the water becomes even more concentrated, eventually rare and unusual minerals such as borax or hanksite will crystallize too. Hanksite crystals can be large and well formed, but are not very complex. Hanksite makes a good addition to any mineral collection.
PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS:
- Color is colorless, white, gray, green or yellow; rarely black.
- Luster is vitreous
- Transparency: Crystals are transparent to translucent.
- Crystal System is hexagonal; 6/m 2/m 2/m.
- Crystal Habits include the typical hexagonal dipyramid terminating an hexagonal prism. The pyramids are often truncated by pinacoids. The six faces of the pyramids are aligned with the six faces of the prism. Tabular and twinned crystals are also common.
- Cleavage is perfect in one direction.
- Fracture is uneven.
- Hardness is 3 - 3.5
- Specific Gravity is approximately 2.5 (slightly below average).
- Streak is white.
- Other Characteristics: Has a salty
taste , a white powdery film will often cloud crystals and some specimens arefluorescent yellowish-white under longwave ultraviolet light. - Associated Minerals are halite, borax, trona, nahcolite, tincalconite and other evaporite minerals.
- Notable Occurrences include the type locality of Searles Lake, San Bernardino County as well as Mono Lake, Mono County, California and other evaporite locations.
- Best Field Indicators include crystal habit, taste, occurrences and associations.
 Amethyst Galleries' Mineral Gallery MINERALS |

HANKSITE specimen han-5
$ 100.00
$ 100.00
Dims: 6" x 4-1/2" x 3-1/2"
Wt: (over 5 lbs.)
Searles Lake, Trona, California, U.S.A.
This specimen has both the largest cluster and the largest crystal of Hanksite that I have yet seen. The cluster itself weighs in at about 5 lbs. The largest crystal likely takes up 1/3 of that weight-- its diameter measures approximately 4 inches and it rises over 2-1/2 inches out of the cluster! Being clustered, none of the crystals is complete with a double-termination. Only a few, however, have damage, and that damage is minimal. Their crystal faces and edges are rough but complete and all are a gray-green coloration and are translucent. They occur in the hexagonal prisms, each with the basal primary and beveled secondary terminations that are common for this mineral. On the underside of the specimen one can see thin, reddish blades of trona, a sodium carbonate mineral that occurs with Hanksite and other evaporite minerals. This specimen is quite BIG, and has been given the obligatory coating of oil to prevent dehydration.


han-5 ($100.00)
Searles Lake, Trona, California, U.S.A.

HANKSITE specimen han-7
$ 30.00
$ 30.00
Dims: 3.8" x 2.6" x 2.5" (9.7 x 6.6 x 6.4 cm)
Wt: 15.4 oz. (436 g)
Searles Lake, Trona, San Bernardino County, California, U.S.A.
This large hand specimen consists of 2 intergrown Hanksite crystals, both of which are incomplete. The larger crystal makes up almost the entire bulk of the specimen and is much more complete than the smaller crystal, half of which seems to be missing. The large crystal has good hexagonal prismatic form and double pyramidal terminations, one of which is incomplete; it possesses well-defined edges and clean faces that show only a dull waxy luster. The crystal's color is a pale yellow, with hints of green and brown, and it is at least dimly transparent, though it contains many inclusions. There is no trona or other material present on the specimen.


han-7 ($ 30.00)
Searles Lake, Trona, San Bernardino County, California, U.S.A.

HANKSITE specimen han-8
$ 27.00
$ 27.00
Dims: 3.5 x 2.4 x 2.2" (8.9 x 6.1 x 2.6 cm)
Wt: 14.4 oz. (408 g)
Searles Lake, Trona, San Bernardino County, California, U.S.A.
This hand specimen basically consists of a single, large hexagonal prismatic Hanksite crystal. It is in excellent condition, showing very little human-induced damage, and has a slightly rounded but very good form, with well-defined edges and relatively clean faces that possess a very dull waxy luster. A few of these faces have other, tiny Hanksite crystals partly embedded in them, but none of these have dimensions that exceed 0.3" (8 mm). The large crystal is capped on either end by hexagonal pyramidal terminations, but due to irregularities in the growth process, one of these is not completely formed (see the close-up image). It has a moderately pale yellow-brown color with a hint of green, and is translucent but shows a dim transparence for a short distance beneath its surface. There is no host rock present.


han-8 ($ 27.00)
Searles Lake, Trona, San Bernardino County, California, U.S.A.

HANKSITE specimen han-9
$ 45.00
$ 45.00
Dims: 3.7 x 2.7 x 2.5" (9.4 x 6.9 x 6.4 cm)
Wt: 1 lb., 2.9 oz. (536 g)
Searles Lake, Trona, San Bernardino County, California, U.S.A.
This rather large hand specimen consists of a cluster of heavily intergown Hanksite crystals. These crystals are in generally good condition, though many of them are rounded or incomplete. All have a the standard hexagonal prismatic form, with hexagonal pyramidal terminations that are truncated with small basal faces. However, the crystals lose definition in form as they decrease in size. All have a dull waxy luster and a gray-green coloration. The crystals are moderately transparent and impressively clear, though the roughness of their faces provides much interference. There are some inclusions, however, which I cannot identify.


han-9 ($ 45.00)
Searles Lake, Trona, San Bernardino County, California, U.S.A.

HANKSITE specimen han-10
$ 45.00
$ 45.00
Dims: 3.4 x 2.5 x 2.0" (8.6 x 6.4 x 5.1 cm)
Wt: 10.8 oz. (305 g)
Searles Lake, Trona, San Bernardino County, California, U.S.A.
At least 8 intergrown Hanksite crystals make up this moderate hand specimen. These crystals are generally in good condition; though several of them are incomplete, there is no fresh or obvious human-induced damage. These crystals have dimensions that range from 0.4 x 0.4 x 0.4" (1.0 x 1.0 x 1.0 cm) to 2.5 x 1.7 x 1.5" (6.4 x 4.3 x 3.8 cm). Though they are very heavily intergrown, most of these still have impressive hexagonal prismatic, double-terminated crystal form, with rounded but definable edges and clean faces that possess a luster ranging from waxy to matte. All have a dull, dirty yellow coloration, but one particular portion of the cluster is stained a dark greenish-black color by either dirt or a material that I cannot identify. The crystals are dimly transparent and contain noticeable cloudy inclusions. There is no host rock present.
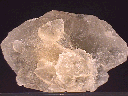
han-10 ($ 45.00)
Searles Lake, Trona, San Bernardino County, California, U.S.A.

HANKSITE specimen han-11
$ 45.00
$ 45.00
Dims: 3.3 x 3.0 x 2.8" (8.4 x 7.6 x 7.1 cm)
Wt: 1 lb., 2.2 oz. (517 g)
Searles Lake, Trona, San Bernardino County, California, U.S.A.
This large hand specimen consists of at least 2 intergrown Hanksite crystals. They are in good condition, though one termination is damaged and said damage might not be very old. These crystals are so heavily intergrown that only a separation at one termination is any evidence of their individuality. Together they form an incomplete crystal that otherwise has good hexagonal prismatic form, with double terminations, rounded but definable edges, and flat, relatively clean faces that possess a dull matte-to-waxy luster. It has a pale yellow-brown coloration with a hint of green and is basically translucent, though some portions have noticeable transparence. There is no host rock present

han-11 ($ 45.00)
Searles Lake, Trona, San Bernardino County, California, U.S.A.

HANKSITE specimen han-12
$ 60.00
$ 60.00
Dims: 3.4 x 3.0 x 2.5" (8.6 x 7.6 x 6.4 cm)
Wt: 15.9 oz. (452.0 g)
Searles Lake, Trona, San Bernardino County, California, U.S.A.
Three or four hexagonal prismatic Hanksite crystals make up this hand specimen. The largest crystal makes up almost the entire mass of the specimen, and the smaller crystals are all heavily intergrown with it. All are in excellent condition, showing no fresh damage, and their form is very good, with slightly rounded but relatively well-defined edges and clean, flat faces that possess a dull waxy luster. All have a dirty yellow-brown coloration that contains hints of green in places where inclusions are located. They show dim transparence that extends less than 1" (2.5 cm) into the crystal. There is no host rock present.


han-12 ($ 60.00)
Searles Lake, Trona, San Bernardino County, California, U.S.A.

HANKSITE specimen han-13
$ 40.00
$ 40.00
Dims: 2.9 x 2.5 x 2.5" (7.4 x 6.4 x 6.4 cm)
Wt: 12.4 oz. (351 g)
Searles Lake, Trona, San Bernardino County, California, U.S.A.
A rather oddly-shaped Hanksite crystal makes up this hand specimen. It is in very good condition, showing no human-induced damage, and actually consists of at least 2 crystals that are so heavily intergrown that they can be construed as a single unit. The crystal appears to have been broken prior to its harvest, as there is a large, uneven depression in one end that has undergone partial healing. Otherwise, it has good hexagonal prismatic, double-terminated form with well-defined edges and clean faces that possess a dull, matte luster. Its color is a dull yellow, but there are some dark green-black patches of discoloration visible within. The crystal is transparent to a degree, but clarity is severely hampered by its luster. As usual, there is no host rock present.

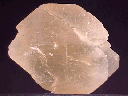
han-13 ($ 40.00)
Searles Lake, Trona, San Bernardino County, California, U.S.A.

HANKSITE specimen han-14
$ 45.00
$ 45.00
Dims: 3.5 x 3.3 x 2.9" (8.9 x 8.4 x 7.4 cm)
Wt: 1 lb., 6.8 oz. (647 g)
Searles Lake, Trona, San Bernardino County, California, U.S.A.
At least 13 intergrown Hanksite crystals make up this hand specimen. The smallest of these has dimensions of 0.5 x 0.3 x 0.3" (1.3 x 0.8 x 0.8 cm), and the largest makes up the bulk of its mass, with dimensions of 3.9 x 3.0 x 2.4" (9.9 x 7.6 x 6.1 cm). All are in very good condition, as damage is minor and limited to 2 of the smallest crystals. Most have good hexagonal prismatic, double-terminated form, but some are very misshapen and nearly amorphous. The largest crystal has the best form, though only one of its pyramidal terminations is complete- this termination is truncated by a small basal face. All of the Hanksites have a dark, dirty greenish-gray coloration and a luster that ranges from waxy to matte. All are translucent at best, but a few of the more exposed crystals contain patches of dim transparence. Clarity, however, is spoiled due to the dull luster. There may be small traces of a trona host rock present, but these are sheltered in crevices and depressions, and look much like the Hanksite itself.


han-14 ($ 45.00)
Searles Lake, Trona, San Bernardino County, California, U.S.A.

HANKSITE specimen han-15
$ 25.00
$ 25.00
Dims: 3.9 x 3.1 x 2.3" (9.9 x 7.9 x 5.8 cm)
Wt: 1 lb., 1.6 oz. (498 g)
Searles Lake, Trona, San Bernardino County, California, U.S.A.
This hand specimen consists almost entirely of a single Hanksite crystal. There are a few other crystals present on the piece, but these are very small compared to the larger one, and are mostly intergrown with it. The crystal is generally in good condition, though there is some damage that likely occurred after harvest. It generally has good hexagonal prismatic form, but only one of its terminations is well-formed. The other is not quite complete due to some growth inconsistencies in one area. Its edges, though, are still well-defined and its faces are clean and possess an oily luster. This luster is caused by oil with which I coated the piece to prevent dehydration. Its color is a dull yellow with a hint of green, and the crystal contains several dark, green-black inclusions that I cannot identify. It is borderline translucent/transparent, with patches of both. As usual, there is no host rock present.


han-15 ($ 25.00)
Searles Lake, Trona, San Bernardino County, California, U.S.A.

HANKSITE specimen han-16
$ 45.00
$ 45.00
Dims: 3.9 x 3.8 x 3.8" (9.9 x 9.7 x 9.7 cm)
Wt: 1 lb., 10.1 oz. (739 g)
Searles Lake, Trona, San Bernardino County, California, U.S.A.
Two discernable Hanksite crystals make up most of this hand specimen. The larger makes up most of the mass of the piece, and has dimensions of 3.8 x 3.8 x 2.7" (9.7 x 9.7 x 6.9 cm), whereas the smaller crystal grows off of the larger and has dimensions of 1.5 x 1.5 x 1.3" (3.8 x 3.8 x 3.3 cm). Both are in good condition, though the larger crystal has some damage that may have occcurred during or after harvest of the specimen. Both have good hexagonal prismatic form with hexagonal pyramidal terminations, but a portion of the large crystal is warped due to its intergrowth with several smaller, warped and broken crystals. Where intact, however, its edges are well-defined and its faces are clean, showing a waxy luster that is brightened by a thin coat of protective oil. All have a dull and dingy yellow coloration, though the large crystal contains areas of dark, green-black discoloration- this discoloration is mostly concentrated around the area of intergrowth with the warped, broken crystals. Other than these areas which show dim translucence to opacity, the crystals are generally dimly transparent. Like most of these specimens, there is no host rock present.


han-16 ($ 45.00)
Searles Lake, Trona, San Bernardino County, California, U.S.A.

HANKSITE specimen han-17
$ 105.00
$ 105.00
Dims: 4.0 x 3.7 x 3.2" (10.2 x 9.4 x 8.1 cm)
Wt: 2 lbs., 2.8 oz. (987 g)
Searles Lake, Trona, San Bernardino County, California, U.S.A.
At least 3 discernable Hanksite crystals are intergrown to make up this large hand specimen. Their visible dimensions range from approximately 1.4 x 1.4 x 1.3" (3.6 x 3.6 x 3.3 cm) to 4.0 x 3.2 x 3.1" (10.2 x 8.1 x 7.9 cm), and all are in very good condition, as they appear to lack any fresh or human-induced damage. The two largest crystals have moderately good double-terminated hexagonal prismatic form- their edges are relatively well-defined and their faces are generally clean and possess a dull waxy-to-matte luster. Like most of the larger specimens I have seen, its color is a dark, dirty greenish-brown and is patchy and uneven. What small amount of clarity can be seen is very dim- the entire piece is generally only translucent, and much of that is rather dim.


han-17 ($105.00)
Searles Lake, Trona, San Bernardino County, California, U.S.A.

HANKSITE specimen han-18
$ 45.00
$ 45.00
Dims: 3.9 x 3.0 x 3.0" (9.9 x 3.6 x 3.6 cm)
Wt: 1 lb., 15.0 oz. (879 g)
Searles Lake, Trona, San Bernardino County, California, U.S.A.
Though at least 5 discernable Hanksite crystals rest on this specimen, most of these measure less than 1" (2.5 cm) along any axis and are heavily intergrown with the largest crystal, which makes up the bulk of the mass of the piece. All are in excellent condition, showing no discernable human-induced damage. Those that are exposed enough possess good double-terminated hexagonal prismatic form, with well-defined edges and relatively clean faces that show a dull waxy-to-matte luster. It has a very patchy and uneven dull, dark green coloration, and though it may show glimpses of a dim transparence in some areas, it is basically only translucent as a whole. There is no host rock present, of course.


han-18 ($ 45.00)
Searles Lake, Trona, San Bernardino County, California, U.S.A.

HANKSITE specimen han-19
$ 75.00
$ 75.00
Dims: 4.5 x 3.7 x 2.5" (11.4 x 9.4 x 6.4 cm)
Wt: 1 lb., 14.3 oz. (858.0 g)
Searles Lake, Trona, San Bernardino County, California, U.S.A.
At least 5 Hanksite crystals are intergrown to make up this hand specimen. None of these are complete due to intergrowth and other growing conditions. The largest of these has dimensions of 3.1 x 2.8 x 2.1" (7.9 x 7.1 x 5.3 cm); the next smallest crystal is nearly the same size, whereas the rest have dimensions that are half of those or less. All are in excellent condition, showing no human-induced damage, and have good hexagonal prismatic form- their edges are relatively well-defined, and their faces are clean and possess a matte-to-waxy luster. Their color is generally gray-green with a hint of yellow, and is patchy and uneven. They are dimly transparent to translucent, and some dark inclusions are visible beneath their surfaces. A small amount of a trona host rock lines the underside of the specimen.


han-19 ($ 75.00)
Searles Lake, Trona, San Bernardino County, California, U.S.A.

HANKSITE specimen han-20
$ 45.00
$ 45.00
Dims: 3.5 x 2.8 x 2.4" (8.9 x 7.1 x 6.1 cm)
Wt: 1 lb., 7.1 oz. (656 g)
Searles Lake, Trona, San Bernardino County, California, U.S.A.
This single Hanksite crystal is incomplete but in excellent condition, showing no human-induced damage. Its lack of completeness is most likely caused by restrictions in its growing environment. It has exceptional hexagonal prismatic form, and is effectively doubly-terminated, though one of the terminations is mostly incomplete. Its edges are very well-defined and its faces are slightly striated and quite clean, possessing a waxy luster. They are also slightly oily to the touch, as I have coated the crystal with a protective layer of mineral oil to prevent dessication. Its color is a dull yellow-green that is patchy and dark in places due to pervasive inclusions, and it is moderately to dimly translucent. There is only a tiny amount of trona attached to the crystal at its incomplete area.


han-20 ($ 45.00)
Searles Lake, Trona, San Bernardino County, California, U.S.A.

HANKSITE specimen han-21
$ 90.00
$ 90.00
Dims: 5.0 x 4.0 x 3.2" (12.7 x 10.2 x 8.1 cm)
Wt: 3 lbs., 4.9 oz. (1.499 kg)
Searles Lake, Trona, San Bernardino County, California, U.S.A.
At least 7 intergrown Hanksite crystals make up this large hand specimen. Though they are incomplete due to their intergrowth with each other, all are in excellent condition, showing almost no damage. Their hexagonal prismatic forms are excellent- all have well-defined edges and clean faces that show a dull waxy luster. Their luster would be even duller were it not for a thin coating of protective oil that I applied to all surfaces. Their color is a dull greenish-yellow, and many patches of dark discoloration are visible. Portions of some crystals are dimly transparent, but the cluster is essentially translucent as a whole. A small amount of trona rests among some of the smaller crystals on the "underside" of the specimen, but there is no other host or base rock present.


han-21 ($ 90.00)
Searles Lake, Trona, San Bernardino County, California, U.S.A.

HANKSITE specimen han-22
$ 105.00
$ 105.00
Dims: 4.6 x 3.8 x 3.7" (11.7 x 9.7 x 9.4 cm)
Wt: 3 lbs., 12.5 oz. (1.7.6 kg)
Searles Lake, Trona, San Bernardino County, California, U.S.A.
A single incomplete but huge Hanksite crystal makes up almost the entire mass of this small cabinet specimen. It is in excellent condition, showing no visible human-induced damage, and has excellent hexagonal prismatic form where it is intact. Its edges are well-defined, and its faces are clean and possess a dull waxy-to-matte luster. Its incompleteness is caused by its contact with the trona base rock on which the crystal formed- a noticeable amount of white trona is visible on this uneven surface. The Hanksite has a dull yellow-green coloration and is very uneven due to dark inclusions within. It is translucent in most areas and almost transparent in some.

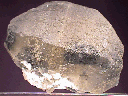
han-22 ($105.00)
Searles Lake, Trona, San Bernardino County, California, U.S.A.

HANKSITE specimen han-23
$ 115.00
$ 115.00
Dims: 4.5 x 4.0 x 3.0" (11.4 x 10.2 x 7.6 cm)
Wt: 3 lbs., 5.2 oz. (1.508 kg)
Searles Lake, Trona, San Bernardino County, California, U.S.A.
This specimen consists almost entirely of a single Hanksite crystal- a few smaller crystals are intergrown with it in one area, but none of these have dimensions that exceed 0.5" (1.3 cm). This large crystal is in excellent condition, showing only a very small amount of damage to a few of its corners, and has well-defined edges and clean faces that possess a dull waxy-to-matte luster. The crystal has the dull, dark yellow-green coloration that is standard for Hanksite from this locality, and contains several small, dark inclusions that I cannot define. The material is not quite transparent, but shows excellent translucence. It is one of the best quality Hanksite crystals of this size that I have seen.


han-23 ($115.00)
Searles Lake, Trona, San Bernardino County, California, U.S.A.

HANKSITE specimen han-24
$ 32.00
$ 32.00
Dims: 3.7 x 2.6 x 2.2" (9.4 x 6.6 x 5.6 cm)
Wt: 1 lb., 4.1 oz. (570 g)
Searles Lake, Trona, San Bernardino County, California, U.S.A.
A single, large Hanksite crystal makes up this specimen. It is in excellent condition, showing only a very small spot of fresh damage, and has excellent hexagonal prismatic form, with well-defined edges, clean faces, and double pyramidal terminations that are truncated by small basal faces. Its luster is dull and waxy at best and its color is a dull yellow-green. Though not completely transparent, it is enough so that one can see the dark greenish-black and white inclusions within. There is no host rock present.


han-24 ($ 32.00)
Searles Lake, Trona, San Bernardino County, California, U.S.A.