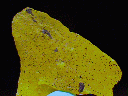
THE MINERAL STURMANITE
THE MINERAL STURMANITE
- Chemistry: Ca6(Fe, Al, Mn)2(SO4)2(B(OH)4)(OH)12 - 26H2O, Hydrated Calcium Iron Aluminum Manganese Sulfate Tetrahydroxoborate Hydroxide.
- Class: Sulfates
- Group: Ettringite
- Uses: Only as mineral specimens.
Specimens
Its chemistry is really interesting. Compared with its close cousin, ettringite, Ca6Al2(SO4)3 (OH)12 - 26H2O, one of the sulfate ion groups has been replaced by the rare ion group, (for lack of a shorter term) tetrahydroxoborate, B(OH)4 with a negative one charge. In addition, four out of every five atoms in this mineral is either a part of a water molecule or an hydroxide and that does not count the hydroxides in the B(OH)4 ion group. It's almost all water! This fact is reflected in its very low specific gravity of only 1.8+, that's less than twice the specific gravity of water.
Some mineral references will list sturmanite's chemistry as Ca6Fe2(SO4)2(B(OH)4)(OH)12 - 26H2O. This formula is written without the manganese and aluminum which do substitute for the iron to an appreciable extent.
It is difficult under ordinary means to distinguish ettringite from sturmanite. Both are members of the Ettringite Group and have similar crystal habit, density, luster and will often share the same bright yellow color.
PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS:
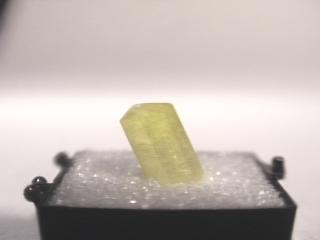
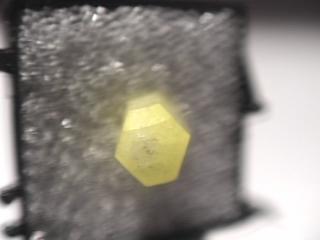
- Color is a bright yellow.
- Luster is vitreous.
- Transparency: Crystals are transparent to translucent.
- Crystal System is trigonal; bar 3 2/m.
- Crystal Habits include hexagonal prisms terminated by an hexagonal pyramid or a pinacoid, more commonly by both. Terminations can be rounded or dome-like but many have nice flat faces. Acicular, platy and fibrous forms are also seen.
- Cleavage is poor and rarely seen.
- Fracture is uneven.
- Hardness is 2.5
- Specific Gravity is approximately 1.8+ (well below average)
- Streak is pale yellow.
- Other Characteristics: Crystals are usually rather small, typically less than 1/4 inch long.
- Notable Occurrences include the Kuruman District, South Africa.
- Best Field Indicators are crystal habit, density, hardness, lack of cleavage, streak and color.