 THE
MINERAL CORNETITE
THE
MINERAL CORNETITE
- Chemistry: Cu3PO4(OH)3, Copper Phosphate Hydroxide.
- Class: Phosphates
- Uses: mineral specimens.
Specimens
Cornetite is a rare secondary copper mineral that is noted for its deep blue, green-blue to green color. It is found in highly weathered, oxidation zones of copper sulfide ore bodies. It has a good deep color, nice crystal forms and an attractive sparkle, all the ingredients for a popular collection mineral.
PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS:
- Color is dark blue, green-blue to green.
- Luster is vitreous.
- Transparency: Specimens are translucent.
- Crystal System: is orthorhombic; 2/m2/m2/m
- Crystal Habits include crystals that are short, rounded, nearly diamond-shaped prisms that are terminated by a dome with trapezohedral faces, also as tiny crystalline druzes, fibrous masses and crusts.
- Cleavage is absent.
- Fracture is uneven.
- Hardness is 4.5
- Specific Gravity is approximately 4.1 (above average for translucent minerals)
- Streak is blue.
- Associated Minerals are limonite, libethenite, malachite, pseudomalachite, brochantite and other secondary copper ore minerals.
- Notable Occurrences include Shaba, Congo; Bwana Mkubwa, Zambia and Empire Nevada Mine, Yerington,Nevada.
- Best Field Indicators are color, streak, crystal habits, associations and density.
 Amethyst Galleries' Mineral Gallery MINERALS |

CORNETITE specimen crn-1
$ 90.00
$ 90.00
Dims: 3.6 x 2.6 x 0.8" (9.1 x 6.6 x 2.0 cm)
Wt: 6.84 oz. (193.9 g)
Likasi, Shaba Province, Zaire
Several clusters and individual crystals of Cornetite rest on the gray shale base of this hand specimen. All are pressed flat against the host rock, and so are not exposed and in excellent condition. The clusters are made up of radiating, compact needles that reach lengths of 0.2" (5 mm), and the individual crystals are shaped more like flattened blades, not exceeding 0.1" (3 mm). All have moderately good orthorhombic form- though the individual crystals are flattened, they appear to have well-defined edges and some clean faces that possess a pearly luster. Their color is a rather deep blue with a hint of green, and though one cannot definitely see as such, I believe that they are translucent. They rest on what I believe is a very thin crust of conichalcite. There may also be a small amount of annabergite present.


crn-1 ($ 90.00)
Likasi, Shaba Province, Zaire

CORNETITE specimen crn-2
$ 90.00
$ 90.00
Dims: 3.9 x 2.9 x 0.9" (9.9 x 7.4 x 2.3 cm)
Wt: 5.45 oz. (154.8 g)
Likasi, Shaba Province, Zaire
Several dozen very small Cornetite blades rest flat against the gray shale base of this specimen. These crystals appear to be in very good condition- only those at the edges of the base rock are visibly damaged or incomplete. None of these exceed 0.2" (5 mm) in length or width, and measure only 1 or 2 mm in thickness. Their orthorhombic bladed form appears to be good, though most are somewhat warped due to flattening and intergrowth. There are a few well-defined edges visible, however. All have a deep blue coloration with a hint of green and a pearly-to-matte luster, and are likely translucent, though this is difficult to determine. An extremely thin layer of another copper-based mineral separates most of the Cornetites from the shale base- I cannot identify this other mineral.

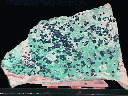
crn-2 ($ 90.00)
Likasi, Shaba Province, Zaire

CORNETITE specimen crn-3
$ 48.00
$ 48.00
Dims: 1.6 x 1.3 x 0.8" (4.1 x 3.2 x 2.0 cm)
Wt: 15 g
Musonoi Mine, Shaba Province, Republic of Congo
A crust of nearly microscopic Cornetite crystals almost completely covers the dull brown base rock of this thumbnail specimen. The crust appears to be in good condition, but the crystals therein are too small to be studied even with a loupe. They likely have good orthorhombic form, however, as they appear to be uniform in size and shape. Their deep aqua-blue color is standard for the specie, and their pearly luster produces a tiny, dull sparkle.

crn-3 ($ 48.00)
Musonoi Mine, Shaba Province, Republic of Congo

CORNETITE specimen crn-4
$ 120.00
$ 120.00
Dims: 3.5 x 2.5 x 1.0" (8.8 x 6.5 x 2.6 cm)
Wt: 3.8 oz. (107 g)
Katanga, Republic of Congo
This cabinet specimen consists of layered Cornetite crusts that coat each side of a tenorite (copper oxide) crust. Actually, the Cornetite itself likely comprises only the outermost layer on the crust, as it has the proper deep blue color. It also shows a dull sparkle that is caused by the presence of countless microscopic crystals. These crystals are far to small to study with a loupe but appear to have at least a pearly luster. I think that this Cornetite layer covers alternating layers of malachite, chrysocolla and/or likely more layers of Cornetite.

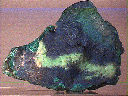
crn-4 ($120.00)
Katanga, Republic of Congo

CORNETITE specimen crn-5
$ 30.00
$ 30.00
Dims: 1.7 x 1.1 x 0.9" (4.3 x 2.7 x 2.4 cm)
Wt: 21 g
Katanga, Republic of Congo
Likley the most unusual Cornetite specimen that I have seen, this small hand piece consists of a botryoidal Cornetite crust that coats a rough tenorite base. The Cornetite crust is damaged in a few places, missing bits of the crust. It has the standard deep aqua-blue coloration of its specie and a pearly luster, and exhibits the nodular, grape-like form of all botryoidal minerals. The material is translucent.

crn-5 ($ 30.00)
Katanga, Republic of Congo

CORNETITE specimen crn-7
$ 50.00
$ 50.00
Dims: 3.4 x 1.4 x 0.4" (8.6 x 3.6 x 0.9 cm)
Wt: 1.4 oz. (40 g)
Likasi, Shaba Province, Zaire
Scores of clustered and individual Cornetite crystals rest on the shale base of this small cabinet specimen. They are in very good condition- damage is sparse- and do not generally exceed 0.1" (2 mm) in length. Due to a restrictive growing environment, their orthorhombic form is not very good. All have the deep aqua-blue color and vitreous luster that are common for Cornetite, and are likely translucent. A few veins of what appears to be turquoise or perhaps pseudomalachite. extend through the shale host rock.


crn-7 ($ 50.00)
Likasi, Shaba Province, Zaire

CORNETITE specimen crn-8
$ 45.00
$ 45.00
Dims: 1.7 x 1.2 x 0.4" (4.4 x 3.0 x 0.9 cm)
Wt: 0.5 oz. (14 g)
Likasi, Shaba Province, Zaire
This small, partly cut shale slab serves as a base for several Cornetite clusters. These clusters are in excellent condition and reach lengths of 0.5" (1.2 cm). The crystals therein show fair to poor orthorhombic form due to restricted growth and intense intergrowth with each other. All have a deep green-blue coloration and a vitreous luster, and are likely translucent. The clusters are accompanied by a small patch of essentially microcrystalline pseudomalachite.

crn-8 ($ 45.00)
Likasi, Shaba Province, Zaire

CORNETITE specimen crn-9
$ 45.00
$ 45.00
Dims: 1.7 x 1.3 x 0.4" (4.4 x 3.2 x 1.0 cm)
Wt: 1.0 oz. (28 g)
Likasi, Shaba Province, Zaire
This large hand specimen consists of a few dozen Cornetite clusters that lay flat on a shale base. The clusters are in very good condition and reach diameters of 0.2" (5-6 mm). The crystals that make up these clusters are heavily intergrown and flattened due to lack of growing space and thus do not have good orthorhombic form. All have the standard deep aqua-blue coloration and vitreous luster, and are accompanied by what is likely a thin dusting of microcrystalline pseudomalachite that coats the shale base rock. This base is firmly affixed to an acrylic base with a hot glue.

crn-9 ($ 45.00)
Likasi, Shaba Province, Zaire

CORNETITE specimen crn-6
$ 60.00
$ 60.00
Dims: 4.7 x 3.0 x 0.4" (11.8 x 7.6 x 1.0 cm)
Wt: 4.0 oz. (113 g)
Likasi, Shaba Province, Zaire
This large cabinet specimen consists of a shale slab on which rest many clusters and individual crystals of Cornetite. These clusters are generally in very good condition and reach diameters of 0.3" (7 mm). The crystals are likewise in good condition and reach lengths of 0.1" (3-4 mm). All show only fair orthorhombic form because they formed within a thin crevice between their base and other layers of shale. All have the classic dark green-blue color and vitreous luster that are standard for their specie and are likely translucent. Other secondary minerals have given part of the shale base a green coloration.

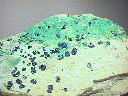
crn-6 ($ 60.00)
Likasi, Shaba Province, Zaire

$ 275.00
Dims: 2.4x2.7x2.0" (6.2x6.8x5.1cm)
Wt: 9.05 oz. (256g)
Katanga, Congo
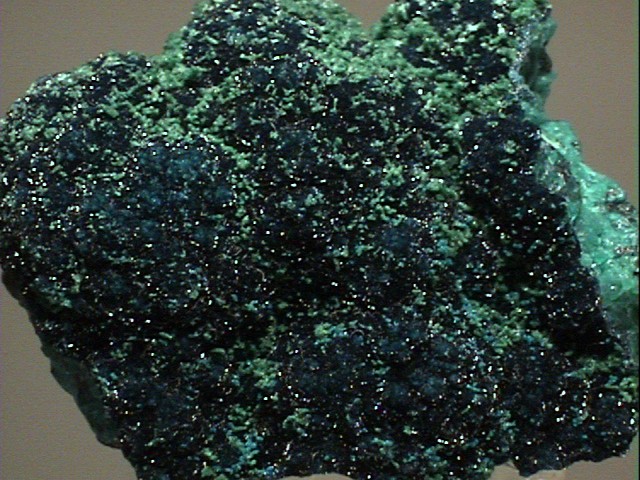
This is a beautiful cabinet specimen of cornetite. The bulk of the specimen is a host rock and layers of a black mineral, likely massive brochantite. A significant fraction of the specimen is massive cornetite, although there is a small amount of chrysocola and malachite present. The cornetite is botryoidal and deep sea blue in color (it reminds me of the deep blue ocean off Hawaii). THe surface terminations are lustrous and sparkly, in several shades of velvety blue, and the protected areas have a lovely scattering of tiny bright green malachite crystals to add more color and contrast. The darker blue areas are likely a mixture of cornetite and brochantite crystals. There are a few small areas of damage, and the back and a side are fractures, and otherwise this specimen is magnificent.


Katanga, Congo

CORNETITE specimen crn-11
$ 30.00
$ 30.00
Dims: 1.30x1.18x0.71" (3.30x3.00x1.81cm)
Wt: 0.58oz (16.3g)
Shaba, Congo
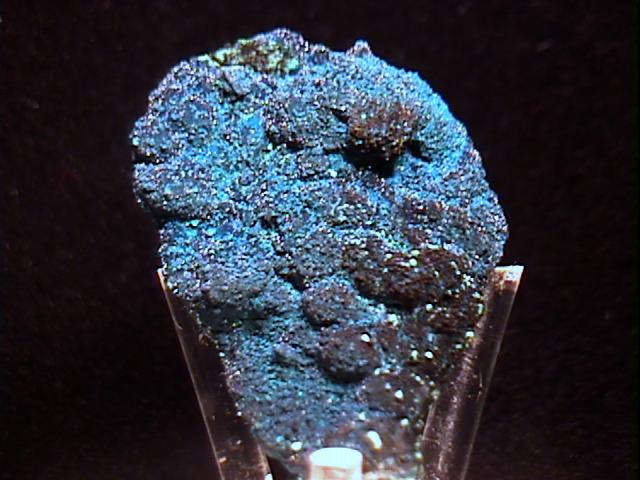
This is a beautiful specimen from the rich mining district of Shaba, Congo (formerly Katanga, Zaire). It displays multiple colorful copper minerals, especially deep blue cornetite crystals as a shell over the host mineral (which looks like chrysocola, but it may be another turquoise blue copper mineral) which in turn is wrapped around a core of something black and metallic looking, and on top of the cornetite are light green tufts that I believe are brochantite, plus tiny crystal clusters of light blue (or is that deep turquoise) that appear to be plancheite. This is a lovely specimen to examine with a loupe, but the only mineral classification I am certain of is the cornetite.

crn-11 ($ 30.00)
Shaba, Congo

CORNETITE specimen crn-12
$ 45.00
$ 45.00
Dims: 1.91x1.32x0.72" (4.86x3.36x1.82cm)
Wt: 1.06oz (30.0g)
Shaba, Congo
This is another beautiful specimen of cornetite. This specimen may be mostly cornetite - at least the surface is, and the cornetite is deep blue clusters of translucent crystals that are so small that I cannot see their shape. There are other minerals, including turquoise colored plancheite crystals, pale turquoise colored opaque crusts, and something black. The black mineral may be the core of the specimen, as the blue crystals rest on top of the black ones. On the other hand, in many places the tiny clusters of lustrous black minerals have the exact shape, size, and luster of the blue cornetite.
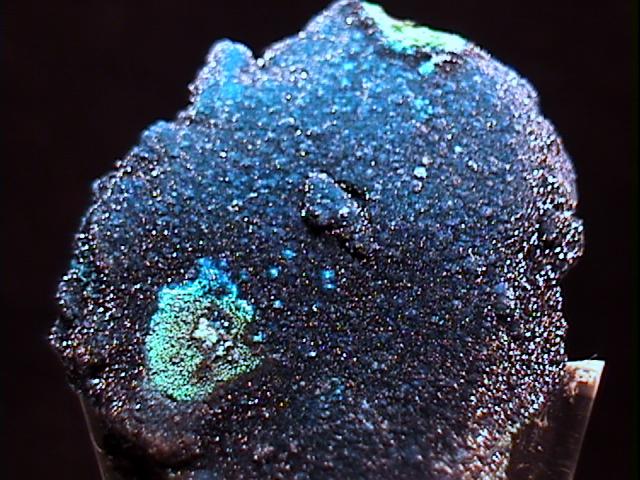

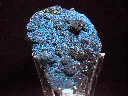
crn-12 ($ 45.00)
Shaba, Congo

CORNETITE specimen crn-13
$ 68.00
$ 68.00
Dims: 1.83x1.11x1.08in (4.65x2.82x2.74cm)
Wt: 1.16oz (33.0g)
Starr Mine, Katanga Province, Congo
Most of one surface of this specimen is covered with cornetite. My loupe reveals that the individual crystals are vitreous and likely transparent, although the color is so deep as to make that difficult to discern. The over-all appearance is slightly dull, and a loupe shows that this is due to many tiny crystals of other minerals including plancheite and malachite. Some areas of the specimen may have additional minerals such as chrysocolla, brochantite, and/or pseudomalachite.


crn-13 ($ 68.00)
Starr Mine, Katanga Province, Congo