THE MINERAL THAUMASITE
THE MINERAL THAUMASITE
- Chemistry: Ca3Si(CO3)(SO4)(OH)6 - 12H2O, Hydrated Calcium Silicon Carbonate Sulfate Hydroxide.
- Class: Sulfates
- Group: Ettringite
- Uses: Only as mineral specimens.
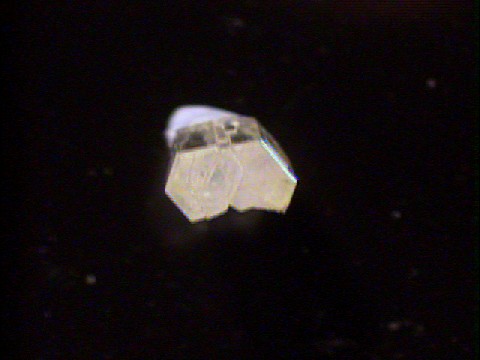
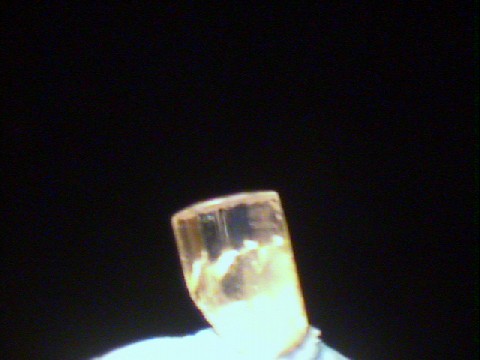
Specimens
Four out of every five atoms in this mineral is either a part of a water molecule or an hydroxide. It's almost all water! This fact is reflected in its very low specific gravity of only 1.9, that's less than twice the specific gravity of water.
PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS:
- Color is colorless or white.
- Luster is vitreous.
- Transparency: Crystals are translucent.
- Crystal System is trigonal; bar 3 2/m.
- Crystal Habits include acicular crystals and massive forms.
- Cleavage is poor and rarely seen.
- Fracture is uneven.
- Hardness is 3.5
- Specific Gravity is approximately 1.9 (well below average)
- Streak is white.
- Associated Mineral is commonly
spurrite . - Notable Occurrences include Crestmore, Riverside Co., California and Paterson, New Jersey, USA and Langban, Sweden.
- Best Field Indicators are density, hardness and association.