 THE MINERAL LEPIDOLITE
THE MINERAL LEPIDOLITE
- Chemistry: KLi2Al(Al, Si)3O10(F, OH)2, Potassium lithium aluminum silicate hydroxide fluoride.
- Class: Silicates
- Subclass: Phyllosilicates
- Group: Micas
- Uses: ore of lithium, ornamental stone and heat insulator for industrial purposes.
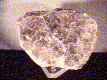
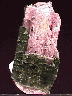
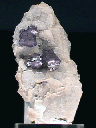
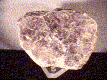
Specimens
Lepidolite, like other micas, has a layered structure of lithium aluminum silicate sheets weakly bonded together by layers of potassium ions. These potassium ion layers produce the perfect cleavage. lepidolite crystals accompany such other lithium bearing minerals such as tourmaline, amblygonite and spodumene and can add greatly to the value of these specimens. A rock made of granular pink lepidolite and red to pink tourmaline is used as an ornamental stone for carving. Single large plates or "books" of lepidolite can have appealling violet color and make attractive mineral specimens.
PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS:
- Color is violet to pale pink or white and rarely gray or yellow.
- Luster is vitreous to pearly.
- Transparency crystals are transparent to translucent.
- Crystal System is monoclinic; 2/m
- Crystal Habits include tabular to prismatic crystals with a prominant pinacoid termination. Lepidolite's four prism faces and two pinacoid faces form pseudo-hexagonal crystal "books". The sides of the crystal often tend to tapper. Also as micaseous, lamellar or granular rock forming masses.
- Cleavage is perfect in one direction producing thin sheets or flakes.
- Fracture is not readily observed due to cleavage but is uneven.
- Hardness is 2.5.
- Specific Gravity is approximately 2.8+ (average)
- Streak is white.
- Associated Minerals are quartz, feldspars, spodumene,
ambygonite and tourmaline especially elbaite. - Other Characteristics: cleavage sheets are flexible and elastic, meaning they can be bent and will flex back to original shape.
Also some specimens may show
triboluminescence . - Notable Occurrences include Brazil; Ural Mountains, Russia; several African localities and California, USA.
- Best Field Indicators are crystal habit, color, cleavage, elastic sheets and associations.