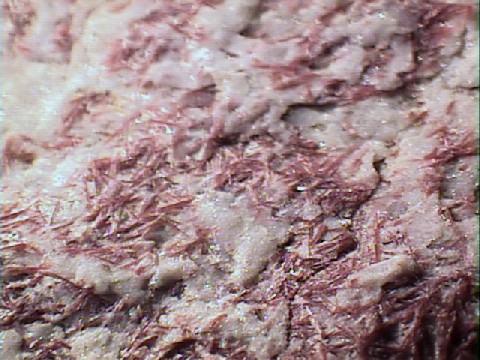
THE MINERAL DUMORTIERITE
THE MINERAL DUMORTIERITE
- Chemistry: Al6.5 - 7(BO3)(SiO4)3(O, OH)3, Aluminum Boro-silicate Hydroxide.
- Class: Silicates
- Subclass: Nesosilicates
- Uses: As an ornamental and semi-precious stone, in the manufacture of high grade ceramics and porcelain and as mineral specimens.
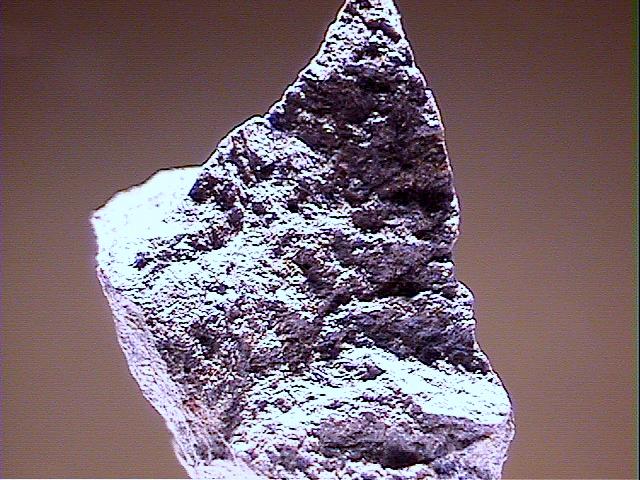
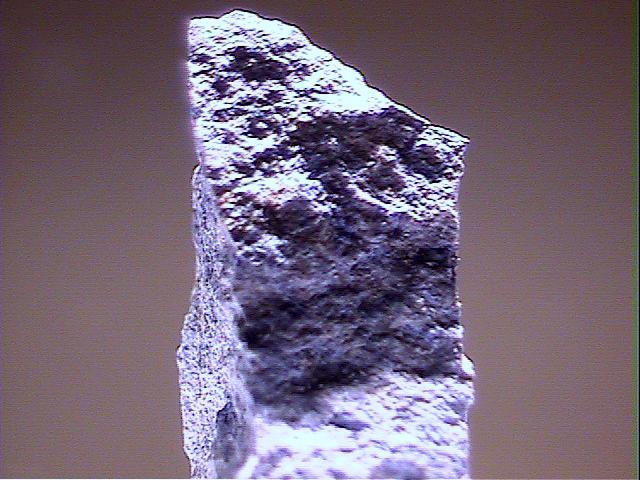
Specimens
Dumortierite is related to several other
nesosilicate boro-silicates such as
PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS:
- Color is typically blue to violet, but also pink and brown.
- Luster is vitreous to dull.
- Transparency: Crystals are translucent to transparent, massive specimens are nearly opaque.
- Crystal System is orthorhombic; 2/m 2/m 2/m.
- Crystal Habits include prismatic crystals but more commonly massive, columnar and fibrous.
- Cleavage good in one direction and poor in four others, but rarely seen.
- Fracture is uneven to hackly.
- Hardness is 7 - 8.5
- Specific Gravity is 3.3 - 3.4
- Streak is bluish white.
- Other Characteristics: Crystals are pleochroic from red to blue to violet. Some specimens fluoresce a blue color under longwave UV light with a fluorescent yellow matrix and a few specimens from Oreana, Nevada have fluoresced white under shortwave UV light.
- Associated Minerals are numerous and include quartz, kyanite, sillimanite, staurolite, andalusite, muscovite, lazulite and pyrophyllite
- Notable Occurrences include the type locality of Beaunan, France as well as Quartzite, La Paz County, Arizona; Colorado; Oreana, Nevada; New York, New York and Alpine, San Diego County and Los Angeles County, California, USA; Magadanskaya, Siberia, Russia and Sahatany, Madagascar.
- Best Field Indicators include hardness, color, density, fluorescence, fibrous crystal habit and environment.