 THE MINERAL CAVANSITE
THE MINERAL CAVANSITE
- Chemistry: Ca(VO)Si4O10(H2O)4, Hydrated Calcium Vanadium Silicate.
- Class: Silicates
- Subclass: Phyllosilicates
- Uses: mineral specimens.
Specimens
Cavansite is a beautiful and rare mineral.
It was only discovered in the last 30 years and is found in only a few locallities.
By far the best crystals come from the famous zeolite quarries in Poona, India.
Crystal aggregates consist of spherical rosettes with jutting pointed crystals.
The deep blue color of even the smallest cavansite crystals is truly amazing.
A beautiful blue cavansite rosette perched on top of the muted colors of the typical
PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS:
- Color is greenish-blue to ocean blue.
- Luster vitreous to pearly.
- Transparency transparent to translucent.
- Crystal System: Orthorhombic
- Crystal Habits radiating acicular crystals forming spherical crystal clusters.
- Cleavage perfect in one direction.
- Fracture conchoidal.
- Hardness 3 - 4
- Specific Gravity is approximately 2.33
- Streak is blue.
- Associated Minerals include zeolites such as stilbite and heulandite as well as calcite, apophyllite , babingtoniteand quartz.
- Other Characteristics: larger crystals show an unusual internal reflection.
- Notable Occurrence is Poona, India and Columbia Co. and Malheur Co., Oregon, USA.
- Best Field Indicators are color, associations, locality and crystal habit.
 Amethyst Galleries' Mineral Gallery MINERALS |

$ 120.00
Dims: 4-1/2" x 2-1/2" x 2"
Wt: 9.9 oz
Poona, India
One of our larger specimens of Cavansite, this piece has over 20 separate clusters of the mineral on a bed of stilbite that covers most of the basalt host rock. Though small (not exceeding 1/4 inch in diameter), most of the clusters are undamaged and easy to see, with a few whose crystals have intersected those of the stilbite. The stilbite crystals themselves are also in excellent condition, with minor damage to a few, and lengths of 3/4 inch or less. This is quite pleasant to look at!


Poona, India

CAVANSITE specimen cav-17
$ 75.00
$ 75.00
Dims: 4.8" x 3.3" x 2.2" (12.2 x 8.4 x 5.6 cm)
Wt: 13.0 oz. (368 g)
Wagholi, Poona, Maharashtra State, India
This specimen consists of a basalt host rock that is partially covered with a crust made up of hundreds of stilbite crystals that range in length from less than 1 millimeter to nearly 0.5" (1.3 cm). Among these white crystals are at least 20 radiating clusters of acicular Cavansite crystals. These clusters range in diameter from 3 or 4 millimeters to about 0.3" (8 mm), and have crystals with lengths that are generally half their diameters. The two largest clusters show substantial damage in the form of crushed and broken crystals, but most are in very good condition. Their color is bright blue and they are translucent, with a pearly luster. There is noticeable damage to the crust of stilbites that are intergrown with the Cavansites, but again, most are in good condition.


cav-17 ($ 75.00)
Wagholi, Poona, Maharashtra State, India

CAVANSITE specimen cav-21
$ 100.00
$ 100.00
Dims: 5.0" x 3.3" x 1.9" (12.7 x 8.4 x 4.8 cm)
Wt: 1 lb., 2.8 oz. (532 g)
Poona, Maharashtra State, India
At least 25 radiating clusters of Cavansite needles rest on this large hand specimen. These clusters range in diameter from 0.1 - 0.3" (0.3 - 0.8 cm). About half of the clusters are damaged, showing the radiating habit of the crystals. All have a bright blue color and a pearly luster, and are at least translucent. They rest amid a cluster of stilbite crystals that have excellent form and reach lengths of up to 0.8" (2.0 cm). The stilbites are a milky-white color and have a pearly luster, and are translucent to dimly transparent. They all rest on a pale brown crust that is made up of hundreds of tiny, intergrown stilbites. This crust coats a basalt host rock which is permeated by many small hollows. Some of these hollows contain radiating clusters of other zeolites with needle-like form.


cav-21 ($100.00)
Poona, Maharashtra State, India

CAVANSITE specimen cav-36
$ 65.00
$ 65.00
Dims: 2.4 x 1.9 x 1.7" (6.2 x 4.7 x 4.4 cm)
Wt: 3.46 oz. (98.3 g)
Wagholi, near Poona, Maharashtra State, India
This hand specimen consists of 2 partial and 2 complete Cavansite clusters that rest on a basalt base. The largest cluster measures 0.3" (0.8 cm) and both of the complete ones are in excellent condition. Each cluster is made up of scores of radiating blades that are difficult to study due to their intergrowth. The clusters have the standard deep, aqua-blue coloration and are dimly translucent. The broken ones give a good view of the radiating nature of the crystals. All rest on a bed of crystalline stilbite that partly coats the basalt.
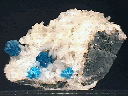
cav-36 ($ 65.00)
Wagholi, near Poona, Maharashtra State, India

CAVANSITE specimen cav-37
$ 100.00
$ 100.00
Dims: 3.8 x 3.2 x 2.1" (9.6 x 8.1 x 5.4 cm)
Wt: 9.1 oz. (259 g)
Wagholi, near Poona, Maharashtra State, India
At least 12 Cavansite clusters and a few loose Cavansite needles rest on the basalt base of this hand specimen. These cluster reach a maximum diameter of 0.3" (0.8 cm) and are generally in good condition, though 2 or 3 appear to be incomplete. All have the standard deep aqua-blue color and pearly luster of their species, and individual crystals are visibly transparent and quite clear. They rest among a bed of large stilbite crystals that covers most of the basalt.

cav-37 ($100.00)
Wagholi, near Poona, Maharashtra State, India

CAVANSITE specimen cav-38
$ 37.50
$ 37.50
Dims: 2.9 x 2.3 x 1.4" (7.3 x 5.7 x 3.6 cm)
Wt: 3.9 oz. (111 g)
Deccan Plateau, near Poona, Maharashtra State, India
At least 6 clusters of radiating Cavansite crystals rest on the basalt base of this hand specimen. These clusters do not exceed 0.4" (1.0 cm) in diameter and are generally in excellent condition, though one of the smaller clusters is obviously damaged. Each contains scores of tiny Cavansite blades, each of which are aggregated with a few others into small "sheaves". Though difficult to study even with a loupe, they likely have good orthorhombic prismatic form. They have a deep aqua-blue color and pearly luster, and though crystals are likely transparent, the clusters are essentially dimly translucent. They are surrounded by many stilbite blades, several of which are broken, that reach lengths of 0.4" (1.0 cm) and have good form. All of these rest on a bed of countless other stilbite blades that do not exceed 2 or 3 mm in length.

cav-38 ($ 37.50)
Deccan Plateau, near Poona, Maharashtra State, India

CAVANSITE specimen cav-41
$ 20.00
$ 20.00
Dims: 0.4 x 0.4 x 0.3" (0.9 x 0.9 x 0.7 cm)
Wt: 1 g
Poona, Maharashtra State, India
A single, incomplete Cavansite cluster comprises this thumbnail piece. It shows considerable damage in one area that was likely caused through removal from its base- this damage enables one to see the compact, radial nature of the cluster. The crystals therein reach only 0.2" (5 mm) in length at most, and are too compact to easily study. All have the standard deep, aqua-blue color and pearly luster, and are likely transparent, though the cluster is only dimly translucent. There is no host rock present.

cav-41 ($ 20.00)
Poona, Maharashtra State, India

CAVANSITE specimen cav-45
$ 25.00
$ 25.00
Dims: 0.4 x 0.3 x 0.3" (1.1 x 0.9 x 0.9 cm)
Wt: 2 g
Poona, Maharashtra State, India
This small thumbnail piece consists of a rounded Cavansite cluster to which is attached a partial stilbite crystal. This cluster measure about 0.3" (9 mm) in diamter and is in very good condition, showing light damage. It is made up of scores of intergrown crystals that appear to have a good orthorhombic prismatic form, though they are rather heavily intergrown. All have the standard deep aqua-blue color and pearly luster of their specie. Though individual crystals are dimly transparent, the cluster is dimly translucent.

cav-45 ($ 25.00)
Poona, Maharashtra State, India

CAVANSITE specimen cav-52
$ 37.50
$ 37.50
Dims: 1.1 x 0.6 x 0.3" (2.8 x 1.5 x 0.8 cm)
Wt: 1 g
Poona, Maharashtra State, India
This small thumbnail specimen consists of a round cluster of radiating Cavansite needles that rests amid a cluster of intersecting stilbite blades. The Cavansite cluster measures 0.3" (8 mm) in diameter and is made up of scores of needles that are rather heavily intergrown. All have the standard deep aqua-blue color and pearly luster and are translucent and difficult to study due to intergrowth. The stilbite blades are in good condition, showing moderate damage. The piece is affixed to a flat acrylic base with a removable putty.
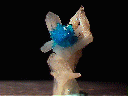
cav-52 ($ 37.50)
Poona, Maharashtra State, India

CAVANSITE specimen cav-53
$ 140.00
$ 140.00
Dims: 3.4x1.9x1.5" (8.7x4.9x3.7cm)
Wt: 2.6 oz. (73.6g)
Poona, Maharashtra State, India
Three beautiful cavansite clusters rest among two dozen large stilbite blades on this specimen. In turn, these minerals are on a druze of small stilbite crystals that cover the host basalt rock. The contrast between the bright blue cavansite balls and the translucent white stilbite is excellent. The three large cavansite balls (and the several other scattered clusters of the mineral) are composed of radial clusters of transparent blue crystals, which are essentially undamaged.


cav-53 ($140.00)
Poona, Maharashtra State, India

CAVANSITE specimen cav-55
$ 30.00
$ 30.00
Dims: 1.9x1.6x1.0" (4.9x4.0x2.5cm)
Wt: 1.25 oz. (35.5g)
Poona, Maharashtra State, India
This specimen features a single spherical cluster of cavansite and a dozen nice stilbite crystals on a basalt base with a druzy crust of more stilbite. The cavansite is excellent, as the deep blue crystals are individually transparent and have a vitreous luster. They are organized in clusters of smaller crystals, all of which appear to radiate from a point. In each cluster, the center crystals are longer, giving each grouping a tapered look. The larger stilbite crystals are also good, with a very white color and a pearly luster.
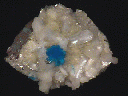
cav-55 ($ 30.00)
Poona, Maharashtra State, India

CAVANSITE specimen cav-54
$ 35.00
$ 35.00
Dims: 2.04x1.94x1.40" (5.19x4.94x3.55cm)
Wt: 2.79oz (79.0g)
Poona, Maharashtra State, India
This specimen contains a single very nice cavansite cluster resting on a stilbite druze on a chunk of basalt. The pretty and very deep blue of the cavansite contrasts nicely with the off-white and translucent stilbite. The cavansite is actually transparent, although the size of the crystals makes this hard to see. The cluster is approximately spherical, and there is quite a bit of variation in the lengths of the individual crystals. It is essentially undamaged.


cav-54 ($ 35.00)
Poona, Maharashtra State, India
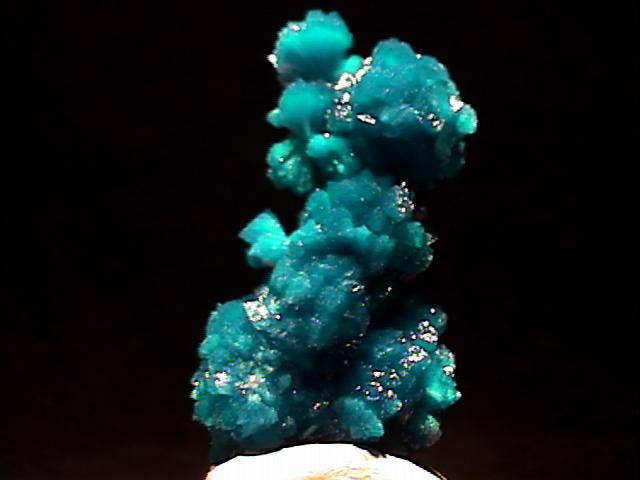

CAVANSITE specimen cav-56
$ 135.00
$ 135.00
Dims: 1.56x0.38x0.24" (3.97x0.96x0.62cm)
Wt: 0.32oz (9.1g)
Wagholi, Poona, India
This is a beautiful specimen of essentially pure cavansite. It is an elongated intergrowth of 5 spherical clusters with several small radial clusters attached. The cavansite is a deep aqua-blue color, translucent and with a vitreous luster. There are only a couple of tiny spots of damage, not readily visible to the unaided eye. A loupe does reveal the presence of some incredibly tiny white needles of some other mineral. This specimen is both more blue and more uniform than the images suggest.
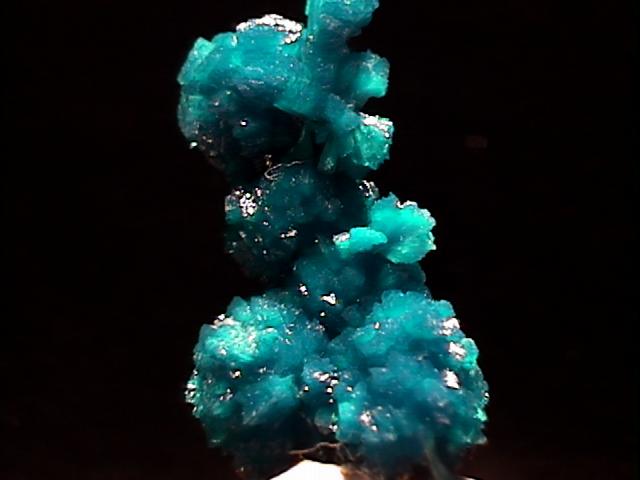


cav-56 ($135.00)
Wagholi, Poona, India
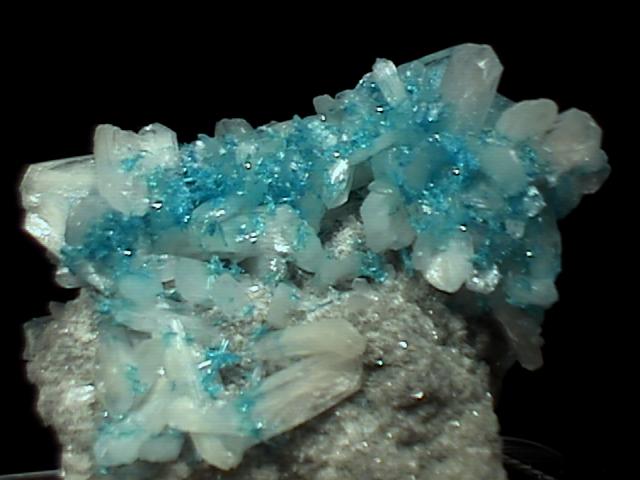

CAVANSITE specimen cav-57
$ 225.00
$ 225.00
Dims: 2.73x1.86x1.56" (6.94x4.73x3.95cm)
Wt: 3.27oz (92.6g)
Deccan Plateau, near Poona, Maharashtra State, India
A newly opened pocket is yielding beautiful cavansite specimens like this one. Instead of tight balls of small crystals, this specimen boasts hundreds of intergrown crystals with exceptional color and clarity. The color is an intense aqua-blue, and the crystals are transparent with a vitreous luster. The individual crystals are large enough to be examined with a loupe, and they are long and prismatic, with a diamond-shaped cross section and a roof termination slanted along its peak. The cavansite crystals rest on a bed of colorless stilbite crystals which are transparent but have a silky luster which prevents (for the most part) seeing through them.
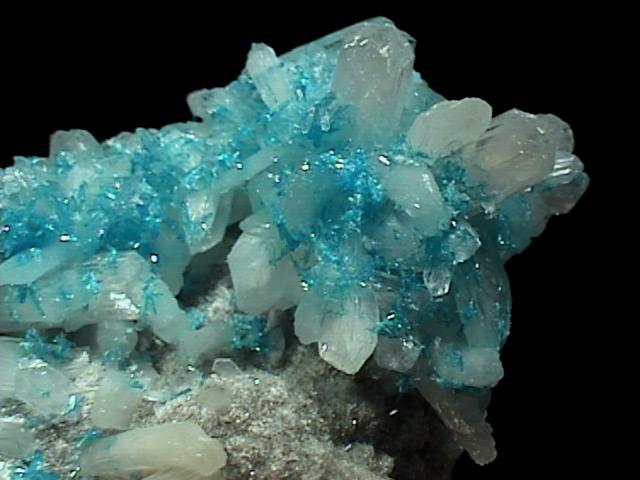

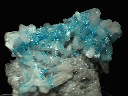
cav-57 ($225.00)
Deccan Plateau, near Poona, Maharashtra State, India
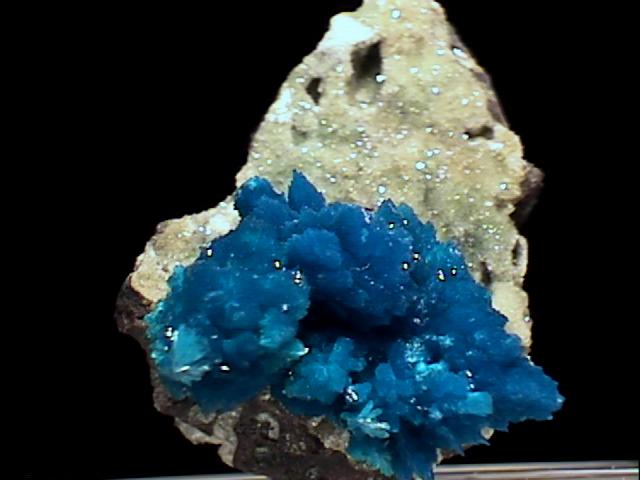

CAVANSITE specimen cav-58
$ 158.00
$ 158.00
Dims: 1.39x1.28x1.01" (3.52x3.24x2.58cm)
Wt: 0.77oz (21.9g)
Wagholi, Poona, India
This is an unusual and pretty specimen of cavansite. Its color is a very deep aqua-blue, and the individual crystals are transparent, although the overall appearance is translucent. These crystals are not organized in spherical clusters - many of them are in parallel clusters nearly vertical to the host rock. Also, many of the crystals are large enough to be examined with the unaided eye, although a loupe does help reveal their clarity and form.
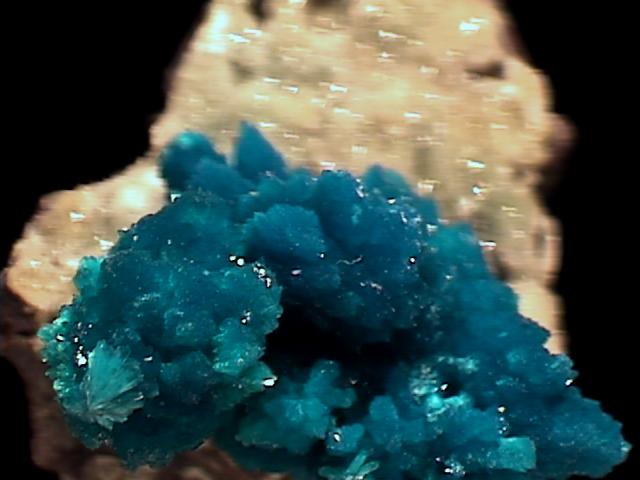


cav-58 ($158.00)
Wagholi, Poona, India
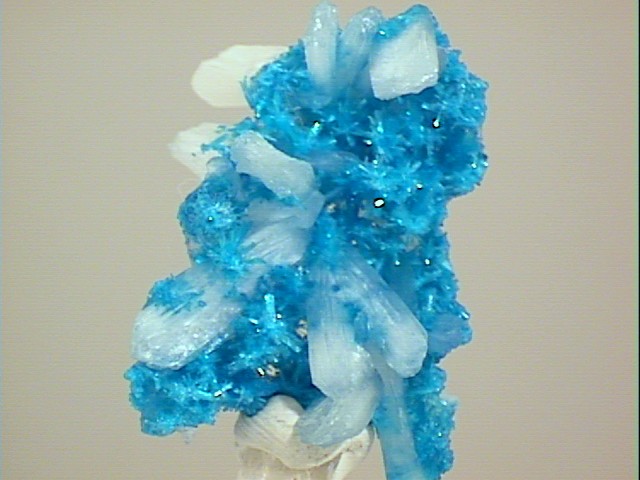

CAVANSITE specimen cav-59
$ 100.00
$ 100.00
Dims: 1.28x0.85x0.51" (3.25x2.17x1.29cm)
Wt: 0.14oz (4.1g)
Deccan Plateau, near Poona, Maharashtra State, India
This specimen has dozens of sparse radial clusters of cavansite crystals. The individual crystals are large enough to be examined, and they are transparent and a deep turquoise blue in color. They have a vitreous luster, and a slant termination, but their cross section is difficult to describe, so I'll just say "complex". Accompanying the cavansite are more than a dozen colorless, silky stilbite crystals. A loupe reveals that the cavansite crystals interpenetrate the stilbite, suggesting that the cavansite formed first, then the stilbite over-grew the cavansite clusters. While this form of cavansite does not display the pretty blue balls of some occurances, the color is exceptionally pretty and the crystals are very lustrous, giving the specimen a lot of sparkle.
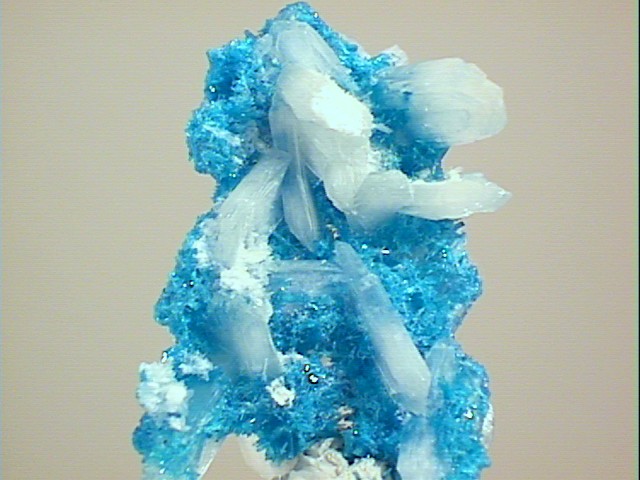


cav-59 ($100.00)
Deccan Plateau, near Poona, Maharashtra State, India

CAVANSITE specimen cav-60
$ 60.00
$ 60.00
Dims: 1.74x1.54x1.45in (4.43x3.92x3.69cm)
Wt: 2.04oz (57.9g)
Deccan Plateau, near Poona, Maharashtra State, India
A beautiful deep aqua-blue ball of canvansite rests on a matrix of basalt covered with a stilbite druze. There is a second, partial cluster of cavansite that is easily examined with a loupe, revealing the transparent nature of the individual crystals.


cav-60 ($ 60.00)
Deccan Plateau, near Poona, Maharashtra State, India