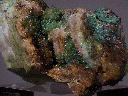 THE
MINERAL TSUMEBITE
THE
MINERAL TSUMEBITE
- Chemistry: Pb2Cu(PO4)(SO4)OH , Lead Copper Phosphate Sulfate Hydroxide
- Class: Phosphates
- Uses: only as a mineral specimen.
Specimens
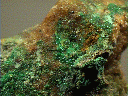
Tsumebite forms good, colorful specimens and is a popular collection mineral, although quite rare. It is closely related to its cousin, arsentsumebite. The two minerals are in a series in which the arsenate ion group in arsentsumebite is replaced by a phosphate ion group in tsumebite. The two differ only slightly mostly because the structure is the same in the two minerals. Both are formed in the oxidation zone of lead-copper ore deposits.
Both minerals are unusual in that they have two ion groups instead of the usual one in most minerals. It the case of tsumebite, it has a phosphate ion group and a sulfate ion group. Mineralogists prefer to classify it as a phosphate because the phosphate ion group has a higher negative charge (-3) than the sulfate group (-2).
PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS:
- Color is emerald green and yellow-green.
- Luster is vitreous.
- Transparency crystals are transparent to translucent.
- Crystal System is monoclinic.
- Crystal Habits include tabular crystals that can form twinned trillings and also as crusts and spherules.
- Cleavage: None.
- Fracture: Uneven.
- Hardness is 3.5
- Specific Gravity is approximately 6.2 (heavy for translucent minerals)
- Streak is green.
- Associated Minerals include azurite, wulfenite, mimetite, cerussite and smithsonite.
- Notable Occurrences are limited to Tsumeb, Namibia and Morenci, Arizona, USA.
- Best Field Indicators are crystal habit, locality, associations, density and color.