THE MINERAL MOTTRAMITE
THE MINERAL MOTTRAMITE
- Chemistry: PbCu(VO4)(OH) , Lead Copper Vanadinate Hydroxide
- Class: Phosphates
- Group: Descloizite
- Uses: As a minor ore of lead and copper and as mineral specimens
- Specimens
Mottramite is an end member of a series composed of the mineral
descloizite.
Mottramite is the copper rich end member while descloizite is the zinc rich member.
Both minerals usually contain significant percentages of both elements and are rarely pure.
Mottramite is the rarer of the two minerals.
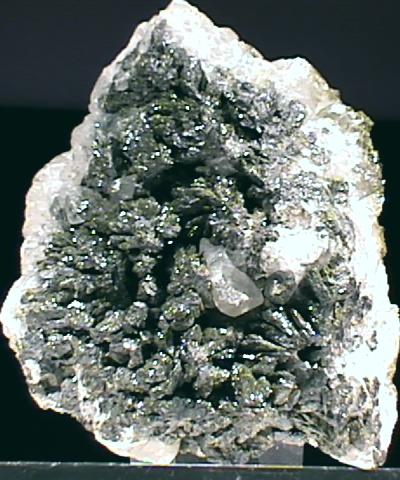
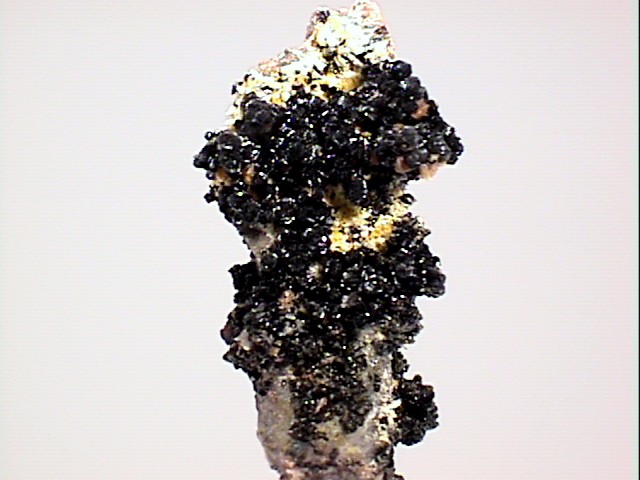
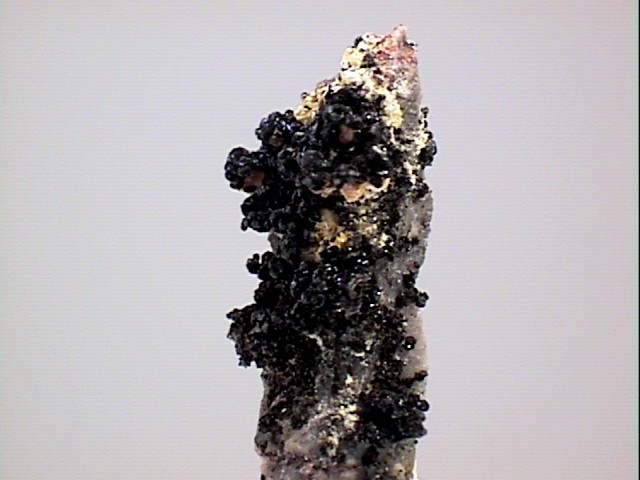
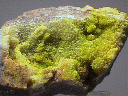
Mottramite can form sparkling crusts that have a nice luster and striking green color.
Its rarity and attractiveness are the reason for the typically high prices one would expect to pay for a fine specimen.
PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS:
- Color is typically various shades of green, rarely black.
- Luster is resinous.
- Transparency: Crystals are transparent to opaque.
- Crystal System is orthorhombic; 2/m2/m2/m
- Crystal Habits are typically tiny druzy crusts, radiating and stalactitic masses.
- Cleavage is none.
- Fracture is conchoidal to uneven.
- Hardness is 3 to 3.5.
- Specific Gravity is approximately 5.7 - 6 (very heavy for translucent minerals)
- Streak is green.
- Associated Minerals are descloizite, malachite and other secondary ore minerals.
- Notable Occurrences include Pinal County, Arizona, USA; Chile; England; Bolivia and elsewhere.
- Best Field Indicators are color, crystal habit, locallities and density.
 THE MINERAL MOTTRAMITE
THE MINERAL MOTTRAMITE