 THE
MINERAL RUTILE
THE
MINERAL RUTILE
- Chemistry: TiO2, Titanium Oxide
- Class: Oxides and Hydroxides
- Group: Rutile
- Uses: Ore of titanium, pigment and as an ornamental stone when in clear quartz
Specimens
Rutile is an interesting, varied and important mineral. Rutile is a major ore of titanium, a metal used for high tech alloys because of its light weight, high strength and resistance to corrosion. Rutile is also unwittingly of major importance to the gemstone markets. It also forms its own interesting and beautiful mineral specimens.
Microscopic inclusions of rutile in quartz, tourmaline, ruby, sapphire and other gemstones, produces light effects such as cat's eye and asterisms (stars). A beautiful stone produced by large inclusions of golden rutile needles in clear quartz is called rutilated quartz. Rutilated quartz is sometimes used as a semi-precious stone and/or for carvings. This stone is produced because at high temperatures and pressure, n(SiO2)-n(TiO2) is in a stable state but as temperatures cool and pressure eases the two separate with rutile crystals trapped inside the quartz crystals.
Twinning is common in rutile crystals, with a cyclic twin forming that is comprised of six or even eight "twins" arranged in a circle. A Rutile Star is a formation of crystals of rutile in a six rayed orientation. The crystals grow off of a hematite crystal and the orientation is caused by its six rhombic faces.
PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS:
- Color is black or reddish brown in large thick crystals or golden yellow or rusty yellow as inclusions or in thin crystals.
- Luster is adamantine to submetallic.
- Transparency: Crystals are transparent in rather thin crystals otherwise opaque.
- Crystal System is tetragonal; 4/m 2/m 2/m
- Crystal Habits include eight sided prisms and blocky crystals terminated by a blunt four sided or complex pyramid. The prisms are composed of two four sided prisms with one of the prisms being dominant. Crystals with some twins forming hexagonal or octahedral circles. A very common habit is thin acicular needles (especially as inclusions in other minerals) or as blades.
- Cleavage is good in two directions forming prisms, poor in a third (basal).
- Fracture is conchoidal to uneven.
- Hardness is 6 - 6.5
- Specific Gravity is 4.2+ (slightly heavy)
- Streak is brown
- Other Characteristics: Striations lengthwise on crystals, high refractive index (2.63) gives it a sparkle greater than diamond (2.42).
- Associated Minerals are quartz, tourmaline, barite, hematite and other oxides and silicates.
- Notable Occurrences include Minas Gerias, Brazil; Swiss Alps; Arkansas, USA and some African locallities.
- Best Field Indicators are crystal habit, streak, hardness, color and high index of refraction (luster).
 Amethyst Galleries' Mineral Gallery MINERALS |

$ 24.00

rut-1 ($ 24.00)

$ 38.00

rut-2 ($ 38.00)

$ 35.00

rut-3 ($ 35.00)

$ 45.00

rut-4 ($ 45.00)

$ 100.00


$ 75.00

rut-6 ($ 75.00)

$ 60.00


rut-7 ($ 60.00)

$ 36.00


rut-8 ($ 36.00)

$ 36.00


rut-9 ($ 36.00)

$ 40.00
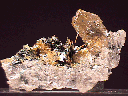
rut-10 ($ 40.00)

$ 45.00

rut-12 ($ 45.00)

$ 36.00

rut-13 ($ 36.00)

$ 30.00
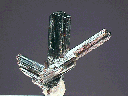
rut-14 ($ 30.00)

$ 90.00

rut-15 ($ 90.00)

$ 28.00
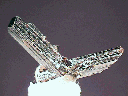
rut-16 ($ 28.00)

$ 32.00
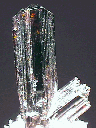
rut-17 ($ 32.00)

$ 55.00

rut-18 ($ 55.00)

$ 66.00


rut-19 ($ 66.00)

$ 36.00

rut-20 ($ 36.00)

$ 48.00

rut-21 ($ 48.00)

$ 29.00
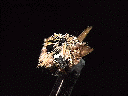
rut-22 ($ 29.00)

$ 54.00


rut-24 ($ 54.00)

$ 25.00
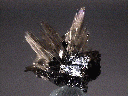
rut-23 ($ 25.00)

$ 84.00


rut-25 ($ 84.00)

$ 60.00

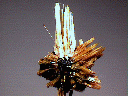
rut-26 ($ 60.00)

$ 29.00
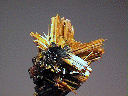
rut-27 ($ 29.00)

$ 84.00


rut-28 ($ 84.00)

$ 25.00


rut-29 ($ 25.00)

$ 84.00


rut-30 ($ 84.00)
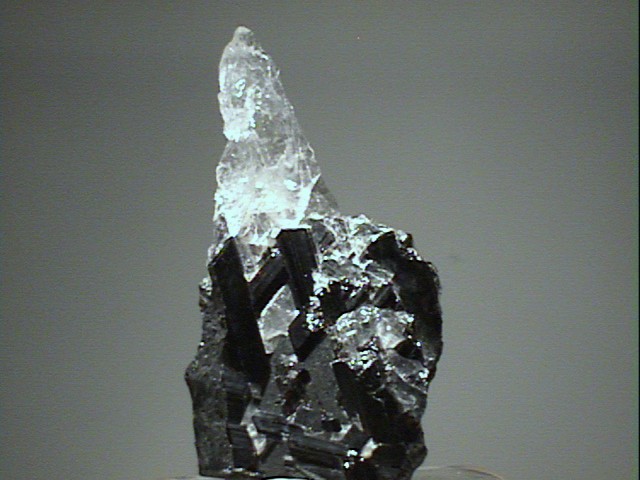

$ 35.00

rut-31 ($ 35.00)
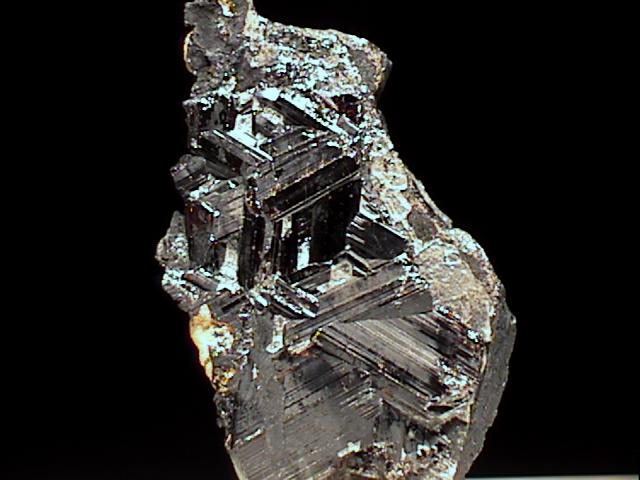

$ 25.00
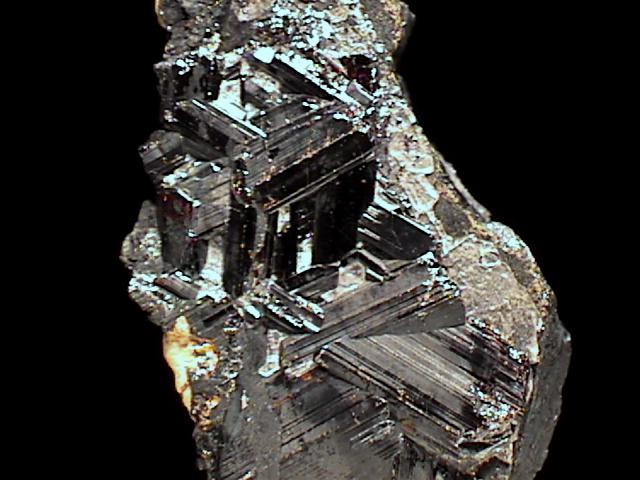

rut-32 ($ 25.00)