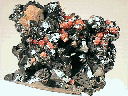THE MINERAL HAUSMANNITE
THE MINERAL HAUSMANNITE
- Chemistry: (Mn+2)(Mn+3)2O 4 , Manganese Oxide
- Class: Oxides
- Uses: a minor ore of manganese and as a mineral specimen.
Specimens
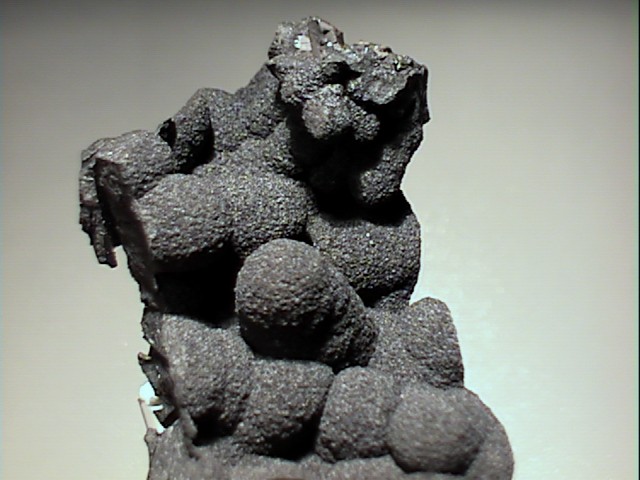
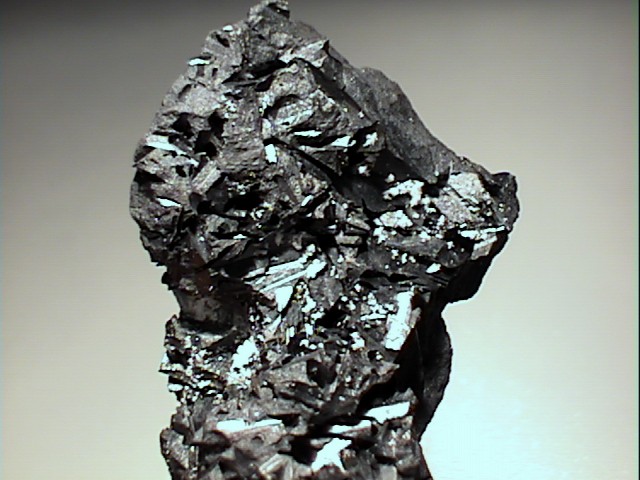
Hausmannite is usually not a beautiful mineral; however some specimens are truly wonderful. It can have a bright metallic luster and form well-shaped crystals. The crystals are tetragonal dipyramids, an eight faced form that looks psuedo-octahedral. Indeed at first look, good crystals of hausmannite appear to be octahedrons like those formed by the spinel group of minerals. The formula of hausmannite, (Mn+2)(Mn+3)2O 4, would also seem to place it in the spinel group. Their general formula is AB2 O4, where A can be a manganese with a positive two charge and B can be a manganese with a positive three (+3) charge. However, those A and B positions are filled with other elements when either one has a manganese ion present. Both sites can not accommodate a manganese ion at the same time and still preserve the isometric structure. Ergo, hausmannite has a distorted spinel structure that produces a tetragonal symmetry and a basal cleavage not possible in the spinel group of minerals. At much higher temperatures, the structure of hausmannite converts to the isometric spinel structure. Hausmannite is an interesting, and can be (when well-formed) a first-rate mineral specimen.
PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS:
- Color is dark brown or black.
- Luster is submetallic to metallic.
- Transparency: crystals are opaque.
- Crystal System: tetragonal; 4/m 2/m 2/m
- Crystal Habits: include the pseudo-octahedral tetragonal dipyramid. Minor pyramidal faces may truncate only the top and bottom points, giving evidence of its tetragonal symmetry instead of the isometric octahedron. Twinning is common and repeated. Also granular and massive.
- Cleavage is perfect in one direction, basal.
- Fracture is uneven.
- Hardness is 5.5
- Specific Gravity is 4.8+ (average for metallic minerals)
- Streak is brown.
- Associated Minerals include psilomelane, pyrolusite, Bixbyite and other manganese minerals.
- Other Characteristics: dipyramid faces might be horizontally striated (not possible on an octahedron).
- Notable Occurrences include Batesville, Arkansas, USA; Ilfeld, Germany; Langban, Sweden and the Ural Mountains, Russia.
- Best Field Indicators are crystal habit, color, hardness, cleavage, density and locality.