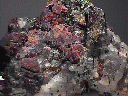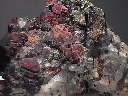 THE MINERAL VILLIAUMITE
THE MINERAL VILLIAUMITE
- Chemistry: NaF, Sodium Fluoride
- Class: Halides
- Group:
Halite - Uses: Rarely cut as gemstones and as mineral specimens.
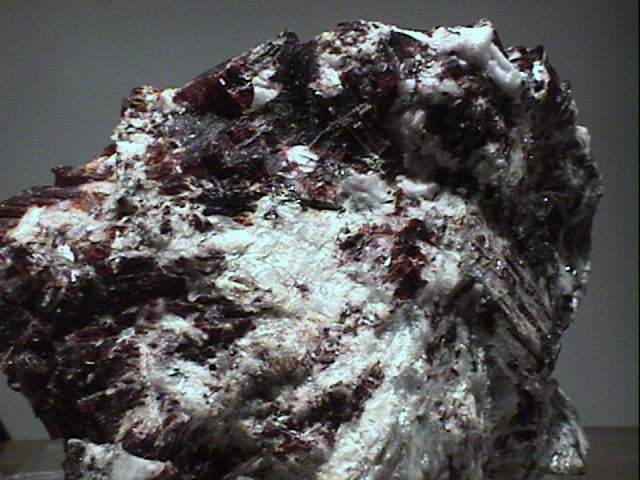
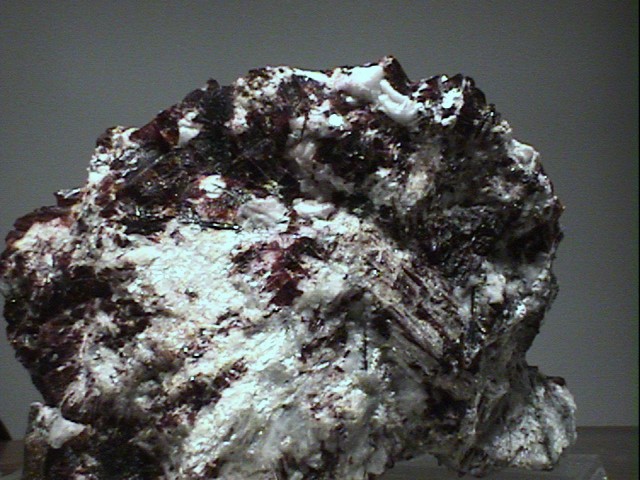
Specimens
Villiaumite was named for the French explorer: Villiaume.
Although he did not techically discover the mineral; he did collect some rock samples from Guinea in which the new mineral villiaumite was found.
Villiaumite is a rare mineral and is found in only a few localities.
Most massive specimens are coming from the
Kola Peninsula where the mineral is
associated with many other rare russian minerals such as
Another great locality for villiaumite is Mont Saint-Hilaire, Quebec, Canada where fine crystals are found. Some crystals from here have been cut as gemstones, but villiaumite is NOT a gemstone mineral as it is too soft and is not durable at all. In fact, villiaumite is soluble in water. Not exactly a property one looks for in a gemstone! Villiaumite is a sodium salt and those salts are usually soluble. And for this reason a desicant should be placed with any specimen to avoid moisture absorbtion and thus its possible destruction.
Villiaumite is a nice mineral to own. It has excellent crystal form (mostly cubes and octahedrons) and is often associated with rare and interesting minerals. Its color is unique and often bright and bold. With rarity, color, associations, fluorescence and crystal form, villiaumite has a lot going for it!
PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS:
- Color is carmine red to reddish orange and lavender pink to pink. Most specimens show some colorless areas.
- Luster is vitreous to waxy in massive specimens.
- Transparency: Crystals are transparent to translucent.
- Crystal System is isometric; 4/m bar 3 2/m.
- Crystal Habits include small cubes, cubo-octahedrons and octahedrons. Also found massive and as void-filling grains.
- Cleavage is perfect in three directions forming cubes.
- Fracture is conchoidal.
- Hardness is 2 - 2.5.
- Specific Gravity is 2.8 (average)
- Streak is pinkish white.
- Other Characteristics: The index of refraction is 1.327, specimens are soluble in water and some specimens weakly fluoresce a red color under UV light.
- Associated Minerals include
calcite,
sodalite,
eudialyte,
nepheline,
aegirine,
pectolite,
lomonosovite , microcline, fluorite,loparite-(Ce) ,lamprophyllite ,vitusite-(Ce) ,steenstrupine-(ce) ,fluorcaphite ,urtite , chkalovite,tuperssuatsiaite ,nefedovite andmurunskite among others. - Notable Occurrences include the type locality: Rouma, the Islands of Los, Guinea as well as the Khibina Massif, Kola Peninsula, Russia; Aris, Namibia; Point of Rocks, Colfax County, New Mexico, USA; Mont Saint-Hilaire, Quebec, Canada and Greenland.
- Best Field Indicators are crystal habit, color, solubility in water, occurrence, fluoresce and associations.