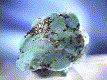
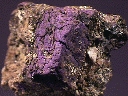- Chemistry: Ca(AsO3OH)-2H2O, Hydrated Calcium Arsenate Hydroxide.
- Class: Phosphates
- Subclass: Arsenates
- Uses: Only as mineral specimens.
Specimens
Pharmacolite is a rather rare arsenic mineral.
It is named from the Greek word for poison in allusion to its arsenic content.
Ironically it is the same word that gives us pharmacy.
There are a couple of other arsenate minerals that have similar names to pharmacolite, namely
pharmacosiderite and
Pharmacolite is related to a few minerals that have a similar formula and structure. Of these only gypsum is common.
- Gypsum CaSO4) - 2H2O
Ardealite Ca2(PO3OH)(SO4) - 4H2OBrushite . Ca(PO3OH) - 2H2O
PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS:
- Color is white, colorless or gray.
- Luster is vitreous to pearly.
- Transparency: Specimens are translucent to transparent.
- Crystal System is monoclinic.
- Crystal Habits include acicular crystals and botryoidal crusts and masses.
- Cleavage is perfect.
- Hardness is 2 - 2.5
- Specific Gravity is approximately 2.7 (average).
- Streak is white.
- Associated Minerals include erythrite and other secondary oxidation minerals.
- Notable Occurrences include Wittichen, Schwarzwald, Germany; Ste. Marie-aux-Mines, Alsace, France and San Gabriel Canyon, California, USA.
- Best Field Indicators: color, crystal habit, locality and associations.